Market Analysis and Insights:
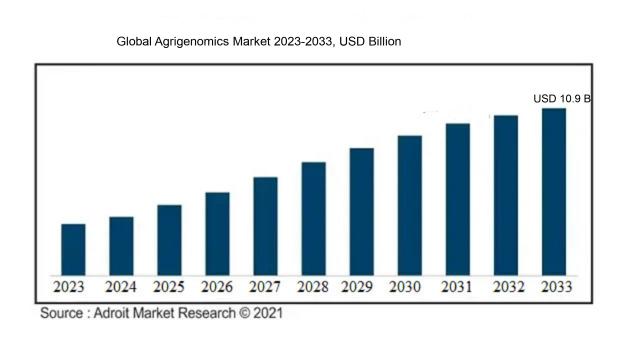
The market for Agrigenomics was estimated to be worth USD 4 billion in 2023, and from 2024 to 2033, it is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 9%, with an expected value of USD 10.9 billion in 2033.
The Agrigenomics sector is significantly propelled by innovations in genomic technologies that facilitate targeted improvements in crops and livestock, aiming to enhance yields and strengthen resistance to diseases and environmental stresses. The escalating global food demand, driven by population growth, calls for creative agricultural solutions, thus spurring research and investment within agrigenomics. Furthermore, a ened consciousness around sustainable farming practices and organic produce encourages the use of genomic methodologies to cultivate eco-friendly agriculture. Support from government programs and financial backing for agricultural research, along with partnerships between biotech companies and academic institutions, accelerates advancements in this field. Additionally, the utilization of big data and artificial intelligence in managing crops and livestock refines decision-making, resulting in more effective and productive agricultural operations. Collectively, these elements are driving the expansion of the Agrigenomics market, positioning it as a vital player in tackling global food security issues.
Agrigenomics Market Scope :
| Metrics | Details |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Historic Data | 2020-2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Study Period | 2023-2033 |
| Forecast Unit | Value (USD) |
| Revenue forecast in 2033 | USD 10.9 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 9% during 2024-2033 |
| Segment Covered | By Genomic Technologies, By Application Areas, By End User, By Service Type, By Project Type, Regions |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America, Middle East and Africa |
| Key Players Profiled | Monsanto Company, DuPont de Nemours, Inc., Syngenta AG, Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, Illumina, Inc., HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology, Agilent Technologies, Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Eurofins Scientific, Genomatix GmbH, Ginkgo Bioworks, Inc., KWS SAAT SE & Co. KGaA, CIMMYT (International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center), and 3M Company. |
Market Definition
Agrigenomics involves the examination of the genetic material of agricultural species, emphasizing the utilization of genomic tools to enhance the characteristics of crops and livestock. This discipline merges molecular biology, genetic science, and bioinformatics to promote food security and the sustainability of agricultural practices.
Agrigenomics is crucial in contemporary agriculture as it utilizes genomic technologies to boost the productivity, durability, and nutritional quality of both crops and livestock. This field facilitates the identification of genetic traits linked to favorable attributes, allowing for targeted breeding methods and shortening the duration required to develop superior varieties. By unraveling the genetic foundations of traits such as disease resistance, adaptability to climate variations, and potential yield, agrigenomics supports the development of sustainable agricultural practices that address the increasing global food requirements. Additionally, it promotes environmental sustainability by reducing reliance on chemical inputs and enhancing biodiversity, thereby contributing to a more robust food system.
Key Market Segmentation:

Insights On Key Genomic Technologies
Next-Generation Sequencing
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) is anticipated to dominate the Global Agrigenomics Market due to its high throughput capabilities, cost-effectiveness, and ability to provide detailed genomic information at an unprecedented scale. The increasing demand for improved crop varieties and the need for personalized agriculture are driving adoption. NGS enables the analysis of complex genomes quickly and with great precision, making it indispensable in genomic research. Moreover, advancements in NGS technologies and their applications in traits discovery, genetic improvement, and disease resistance are solidifying NGS's pivotal role in the agrigenomics landscape, appealing to researchers and agribusinesses alike.
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) remains a critical technique in agrigenomics for amplifying specific DNA s, which is vital for various applications like pathogen detection, genetic fingerprinting, and trait mapping. Despite being slightly overshadowed by the capabilities of NGS, PCR is valued for its simplicity, rapid results, and minimal resource requirements. Its robustness and adaptability make it popular for routine testing in agricultural research. Researchers frequently employ PCR due to its low cost, making it accessible for smaller operations and enhancing its relevance in the agrigenomics market.
Genotyping
Genotyping plays a significant role in the identification of genetic variants within populations, which is crucial for breeding programs and the development of superior crop varieties. By providing insights into the genetic diversity and inheritance patterns of plants, genotyping helps in efficient selection and conservation of germplasm. As the demand for high-yielding, disease-resistant, and climate-adaptive crops increases, genotyping becomes a key tool in enhancing breeding efficiency. Its widespread use in marker-assisted selection has cemented its importance in the agricultural biotechnology sector.
Gene Editing
Gene Editing techniques, such as CRISPR-Cas9, are emerging as groundbreaking tools for precise genetic modifications in plants. While the technique holds significant promise for developing traits like drought tolerance and pest resistance, regulatory challenges and public acceptance remain hurdles. Its ability to create specific genetic alterations without introducing foreign DNA presents a unique advantage, aligning with the goals of sustainable agriculture. As the technology matures and regulatory frameworks evolve, Gene Editing may find broader application in agrigenomics, but currently, it trails behind the more established technologies like NGS.
Insights On Key Application Areas
Crop Improvement
Crop Improvement is expected to dominate the Global Agrigenomics Market, driven by the need to enhance agricultural productivity and food security in the face of rising global population and environmental challenges. This harnesses genomics to develop genetically modified organisms (GMOs) that are more resistant to pests, diseases, and changing climate conditions. As governments and companies invest in advanced research and technology, the crop improvement area is poised for substantial growth. Innovations such as CRISPR and other gene-editing technologies are revolutionizing plant breeding, making it quicker and more efficient, which reinforces the dominant position of this application area.
Livestock Breeding
The Livestock Breeding category focuses on improving animal genetics for production efficiency, disease resistance, and overall productivity. This area has gained traction as livestock producers capitalize on genomic technologies to realize optimal meat, dairy, and egg output. Enhanced breeding programs not only contribute to higher yields but also promote animal welfare and sustainability. The escalating demand for animal protein globally has increased investments in this sector, fueling innovations that promise to redefine livestock management practices.
Plant Pathology
The Plant Pathology sector aims at understanding and combating diseases that threaten crops, which is crucial for maintaining food supply and quality. Advancements in genomics enable researchers to identify genetic markers linked to disease resistance, facilitating the development of resilient crop varieties. As climate change intensifies plant disease outbreaks, the importance of this field is magnified, leading to enhanced funding and research initiatives. Despite being a growing area, it remains smaller in comparison to crop improvement, as crop yield enhancements generally take precedence.
Environmental Sustainability
The Environmental Sustainability dimension is dedicated to improving agricultural practices to lessen environmental impact and ensure long-term ecological balance. This area focuses on utilizing genomic technologies to create sustainable farming systems, enhancing carbon sequestration, and promoting biodiversity. While beneficial for regenerative agriculture, it faces challenges such as slower adoption rates in traditional farming communities and regulatory hurdles. As awareness of environmental issues increases, this is progressively gaining importance but still trails behind crop improvement and livestock breeding in terms of investment and market share.
Insights On Key End User
Agricultural Corporations
Agricultural Corporations are expected to dominate the Global Agrigenomics Market due to their increasing need for advanced genetic research to enhance crop yield, resistance to diseases, and improvement in overall agricultural productivity. As the global demand for food continues to rise, these corporations invest heavily in genomics solutions to develop high-quality seeds and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) that can withstand harsh environmental conditions. Moreover, the collaboration between agricultural corporations and biotechnology firms accelerates technological advancements, making this category crucially influential. Their financial clout and emphasis on R&D further position them as a key driver of growth in this market.
Research Institutes
Research Institutes play a vital role in the advancement of agrigenomics, providing foundational discoveries and innovative technologies. By conducting comprehensive studies on plant and animal genomes, these institutes contribute significantly to sustainable agricultural practices. Their collaborations with government and industry entities make them a trusted source for reliable data and methodologies, boosting overall market development. With ongoing funding and emphasis on public-private partnerships, they continuously enhance the research landscape, influencing trends and strategies.
Government Agencies
Government Agencies are integral to the Agrigenomics sector, focusing on regulatory frameworks, funding initiatives, and policy development. They are crucial in ensuring the safety and ethical standards of genetic modifications and agrigenomics research, which helps bolster public trust. Furthermore, these agencies often partner with research institutions and other organizations to promote scientific advancements while addressing food security and agricultural sustainability, enhancing their impact on industry growth.
Biotechnology Firms
Biotechnology Firms are pivotal in converting genomic research findings into practical applications in agriculture. They specialize in developing biotechnological tools and products that leverage genetic information to create superior agricultural solutions, which enhances productivity and quality. Their innovative approaches enable collaboration with agricultural corporations and research institutes, facilitating the transfer of knowledge and technology. This symbiotic relationship is essential for driving growth and adoption of agrigenomics solutions in the market.
Insights On Key Service Type
Data Analysis Services
Data Analysis Services are anticipated to dominate the Global Agrigenomics Market due to the increasing volume of genomic data generated from sequencing technologies and biotechnology advancements. The demand for actionable insights from complex genomic datasets is surging as agricultural stakeholders aim for enhanced crop yield, disease resistance, and environmental adaptability. Effective data analysis enables precise identification of genetic markers and traits, thereby fostering the development of superior agricultural products. The ability to offer customized solutions based on sophisticated algorithms and artificial intelligence further positions this service as a critical component in agrigenomics, thus driving its market share and relevance.
Genome Mapping Services
Genome Mapping Services play a pivotal role in agrigenomics by providing detailed insights into the genetic architecture of various crops and livestock. These services facilitate the identification of essential genes that govern desirable traits, enabling breeders and researchers to enhance selection processes. As breeding technologies evolve and the need for precision agriculture increases, genome mapping has become crucial for developing genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and hybrid varieties. This remains significant as it lays the foundational knowledge required for downstream applications in breeding programs, although it currently sits in the shadow of data analysis.
Consulting Services
Consulting Services in agrigenomics are experiencing growth as agricultural entities seek expertise in navigating the complex landscape of genomics technologies. These services offer strategic guidance on implementing genomic technologies effectively, addressing regulatory challenges, and aligning R&D with market needs. As the agrigenomics field becomes increasingly sophisticated, organizations are increasingly turning to consultants for insights into best practices and future trends. This service area is invaluable for companies that need tailored advice to optimize their genomic research endeavors, yet it still remains less central than data analysis services.
Sample Preparation Services
Sample Preparation Services are essential for ensuring the integrity and quality of genomic data. These services encompass a range of tasks such as DNA extraction, purification, and validation, which are crucial for successful downstream applications in genomics. As more agricultural companies invest in high-throughput sequencing technologies, the demand for optimized sample preparation processes will undoubtedly rise. However, while important, sample preparation is often considered a preliminary step in the agrigenomics workflow, which limits its overall market dominance compared to more analytical and advisory services within the industry.
Insights On Key Project Type
Commercial Projects
The Global Agrigenomics Market is expected to be dominated by Commercial Projects. This dominance can be attributed to a growing need for sustainable agricultural practices, enhanced crop yields, and the evolving demand for genetically modified organisms (GMOs) to meet food security challenges. As agricultural companies increasingly invest in technological innovations for product development and market application, commercial projects have gained significant traction. Moreover, the rising collaboration between agribusinesses and biotechnology firms fosters a conducive environment for commercial initiatives. With the increasing adoption of agrigenomic techniques in mainstream agriculture and food production, commercial projects are poised to lead the market trajectory in the coming years.
Research Projects
Research Projects play a pivotal role in advancing the field of agrigenomics by driving scientific discovery and innovation. They focus on understanding plant and animal genomics, which is essential for developing resilient crop varieties and livestock breeds. Research endeavors are often supported through governmental and academic institutions, ensuring continuous advancements in genomic technologies. Despite being crucial for the overall progression of the agricultural sector, these projects typically rely on the successful application and commercialization of their findings, which ultimately ties back into the importance of commercial projects in putting new knowledge to practical use.
Collaborative Projects
Collaborative Projects in the agrigenomics sector are increasingly important as they bring together diverse stakeholders, including academic institutions, government agencies, and private companies, to share knowledge and resources. Such partnerships facilitate the pooling of expertise and funding, enabling comprehensive research that may not be feasible for single entities. While they play a significant role in advancing knowledge and addressing complex agricultural issues, their outcomes often hinge on commercial entities applying the research outcomes. Therefore, while collaborative initiatives contribute to the sector's innovation, they tend to be complementary to the more commercially focused activities that drive market growth.
Insights on Regional Analysis:
North America
North America is expected to dominate the global agrigenomics market due to its advanced research infrastructure, significant investment in agricultural biotech, and strong collaboration between public and private sectors. The region boasts some of the leading agrigenomics companies and research institutions that push the boundaries of crop genetic improvement and livestock production. Innovations like genome editing technologies, including CRISPR, are more prevalent in North America, further enhancing its competitive edge. The presence of major agricultural players and a well-established regulatory framework that supports agrigenomic research contribute to this region's dominance.
Latin America
Latin America holds a strong potential in the agrigenomics market, driven by its rich biodiversity and the necessity to improve crop yields to meet the demands of a growing population. Countries like Brazil and Argentina are increasingly investing in agrigenomics to boost agricultural productivity and enhance food security. However, challenges such as regulatory hurdles, limited technological access, and varying degrees of research funding may impede the rapid growth of this. Despite these challenges, the region is making strides, particularly in developing genetically modified crops suited for local conditions.
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region exhibits rapid growth potential in the agrigenomics market, primarily due to its large agricultural sector and the urgent need to combat food security threats. Countries like China and India are significantly investing in agrigenomics to improve crop resilience and productivity. However, the region faces challenges such as varying regulatory environments and limited investment in research facilities. Although promising, market penetration may be inconsistent across different countries in this region, affecting overall dominance in the global agrigenomics landscape.
Europe
Europe is known for its stringent regulations related to genetically modified organisms, which affects agrigenomics market growth. While there is a strong emphasis on sustainable agriculture and environmental concerns, the ambiguity surrounding gene-editing regulations often hampers innovative research within the region. Nonetheless, European companies and research institutions are focused on alternative breeding technologies, which could foster growth. The focus on organic farming and sustainable practices presents unique opportunities, albeit at a slower pace compared to other regions.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East and Africa are emerging players in the global agrigenomics market, largely driven by the need to improve agricultural productivity in arid climates. Governments and organizations are beginning to recognize the importance of agrigenomic research to address food shortages and agricultural challenges. However, limited infrastructure, funding, and political stability remain significant obstacles. While the potential is there, the agrigenomics market in this region will require strategic investments and collaborative efforts to fully tap into its capabilities and meet global demands effectively.
Company Profiles:
The primary contributors to the global agrigenomics market comprise biotechnology companies and agricultural research institutions that spearhead advancements in crop enhancement and resilience against diseases via genomic methodologies. These entities work in partnership with farmers and regulatory authorities to bolster food security and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
Prominent entities within the agrigenomics sector comprise Monsanto Company, DuPont de Nemours, Inc., Syngenta AG, Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, Illumina, Inc., HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology, Agilent Technologies, Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Eurofins Scientific, Genomatix GmbH, Ginkgo Bioworks, Inc., KWS SAAT SE & Co. KGaA, CIMMYT (International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center), and 3M Company.
COVID-19 Impact and Market Status:
The Covid-19 pandemic significantly impacted the global agrigenomics sector by disrupting supply chains, decreasing research investments, and redirecting priorities towards ensuring food security and promoting sustainable agricultural methods.
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound effect on the agrigenomics sector, primarily due to supply chain disruptions and the hindrance of research and development efforts. Lockdowns and safety measures diminished the available workforce, adversely affecting critical field trials and laboratory work necessary for agricultural genomic research. Furthermore, uncertainties regarding funding emerged as both investors and governments shifted their focus to urgent health issues, which resulted in postponements of various agrigenomic initiatives. On the positive side, the pandemic catalyzed the integration of digital technologies and data analytics within the agricultural realm, leading to advancements in crop genomics and precision farming practices. The ened awareness surrounding food security and sustainability during this period spurred increased interest in genetic approaches aimed at improving crop resilience and productivity. Consequently, although the pandemic presented significant challenges, it also opened avenues for progress in gene editing and biotechnology, thereby positioning the agrigenomics industry for potential recovery and growth in the aftermath of the crisis.
Latest Trends and Innovation:
- In September 2023, Illumina announced a partnership with Corteva Agriscience to enhance genomic solutions for crop breeding, combining Illumina's sequencing technology with Corteva's expertise in agricultural sciences.
- In June 2023, Bayer acquired the biotechnology company, CropDesign, to advance its capabilities in plant genomics and accelerate the development of traits for crops aimed at improving yields and resistance to pests.
- In March 2023, Syngenta launched a new genomic breeding platform, Varietal800, designed to facilitate faster development of crop varieties through advanced genomic selection, significantly reducing the time to market for new agricultural innovations.
- In January 2023, Thermo Fisher Scientific completed its acquisition of the genetic analysis firm, Affymetrix, enhancing its offerings in agrigenomics by providing advanced genotyping solutions to agribusiness firms.
- In November 2022, CLC Genomics Workbench released a new version that includes improved features for handling large genomic datasets, catering specifically to the needs of agricultural researchers focused on crop improvement.
- In July 2022, Genomatica entered a collaboration with Wilmar International to develop sustainable agricultural solutions through genomics, focusing on enhancing crop yields while reducing the environmental impact of agriculture.
- In April 2022, the Joint Genome Institute (JGI) of the U.S. Department of Energy announced a significant extension of its plant genomics program, aiming to sequence and analyze multiple staple crops to enhance sustainability and resilience.
- In December 2021, Resilient Genomics secured funding to advance its development of genomic tools for improving the resilience of crops under climate stress, leveraging partnerships with key agricultural stakeholders.
Significant Growth Factors:
The Agrigenomics sector is witnessing expansion fueled by innovations in gene editing techniques, a rising need for sustainable farming practices, and the pursuit of improved crop productivity.
The agrigenomics sector is witnessing significant expansion, propelled by a variety of pivotal elements. Primarily, the urgent need for food security amidst a growing global population has created a demand for innovative agricultural methodologies. Agrigenomics facilitates the enhancement of crop traits and increased productivity through genetic engineering and marker-assisted selection, effectively tackling challenges related to food shortages. Furthermore, there is an increasing focus on sustainable farming techniques and environmentally friendly practices, which is driving investment in genomic technologies that encourage responsible agricultural stewardship.
In addition, breakthroughs in sequencing methods and bioinformatics are substantially lowering costs and enhancing the accessibility of genetic research, resulting in more effective development processes. Government support and funding directed towards agricultural biotechnology are also instrumental in fostering advancements within the market, paving the way for new genomic applications. The rising incidence of plant diseases and pest infestations has escalated the demand for robust crop varieties, a need that agrigenomic approaches can satisfactorily meet. Lastly, the synergy between agrigenomics and precision agriculture technologies is boosting productivity and operational efficiency, rendering this sector an appealing target for agricultural investors. Collectively, these driving forces are advancing the agrigenomics market, steering it towards enhanced adoption and innovation in farming techniques.
Restraining Factors:
The Agrigenomics sector encounters notable hurdles due to intricate regulatory frameworks, elevated research expenditures, and diverse consumer attitudes toward genetically modified organisms.
The agrigenomics sector is confronted with multiple constraints that may hinder its development. Primarily, the substantial expenses linked to research and development, coupled with the sophisticated technologies necessary for genomic analysis, can dissuade smaller enterprises from participating in this market. Moreover, regulatory hurdles, such as rigorous government regulations and the lengthy approval processes for genetically modified organisms (GMOs), present obstacles that stifle innovation and impede market entry. Ethical dilemmas associated with genetic engineering may elicit public apprehension, further restricting consumer acceptance and the uptake of agrigenomic products. Additionally, the deficiency in technical know-how and a thorough grasp of genomic technologies among farmers and relevant stakeholders present formidable challenges to the successful integration of these innovations in agricultural practices. The impacts of climate change and related environmental concerns can also affect crop yields, complicating the prediction of the long-term effectiveness of genomic interventions. Nevertheless, the agrigenomics industry possesses significant promise for promoting agricultural sustainability, enhancing productivity, and ensuring food security, fostering continuous investment and innovation aimed at overcoming these barriers. With ongoing advancements and increasing recognition of the advantages of these technologies, the market is set for steady growth and the creation of pioneering solutions to address sustainable food production challenges.
Key Segments of the Agrigenomics Market
By Genomic Technologies
• Next-Generation Sequencing
• Polymerase Chain Reaction
• Genotyping
• Gene Editing
By Application Areas
• Crop Improvement
• Livestock Breeding
• Plant Pathology
• Environmental Sustainability
By End User
• Research Institutes
• Agricultural Corporations
• Government Agencies
• Biotechnology Firms
By Service Type
• Genome Mapping Services
• Data Analysis Services
• Consulting Services
• Sample Preparation Services
By Project Type
• Research Projects
• Commercial Projects
• Collaborative Projects
Regional Overview
North America
• US
• Canada
• Mexico
Europe
• Germany
• France
• U.K
• Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
• China
• Japan
• India
• Rest of Asia Pacific
Middle East and Africa
• Saudi Arabia
• UAE
• Rest of Middle East and Africa
Latin America
• Brazil
• Argentina
• Rest of Latin America

