Connected Worker Market Analysis and Insights:
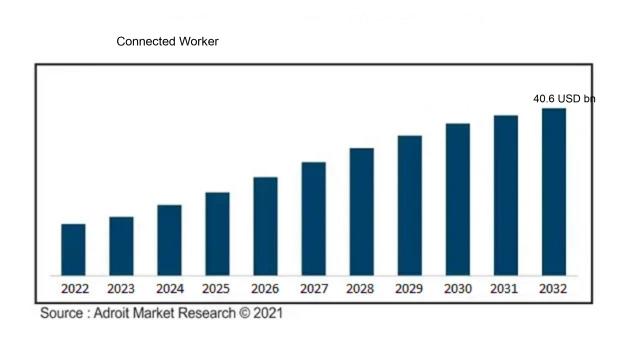
The market for Global Connected Worker was estimated to be worth USD 6.7 billion in 2023, and from 2024 to 2032, it is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 22.9%, with an expected value of USD 40.6 billion in 2032.
The Connected Worker Market is largely propelled by several critical factors, such as the growing emphasis on workplace safety and operational efficiency, advancements in wearable devices, and the emergence of Industry 4.0. Companies are prioritizing increased productivity and minimized downtime, which drives investments in interconnected technologies that allow for instantaneous communication and data exchange among staff. Furthermore, the demand for remote monitoring and assistance, particularly highlighted by recent global transitions toward hybrid work settings, is stimulating growth in this area. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies is also crucial, as it facilitates smooth connectivity and data analysis to enhance decision-making. Additionally, the need for regulatory compliance and the goal of fostering improved employee collaboration and engagement further contribute to the expansion of this market, with organizations seeking innovative solutions to address these challenges. Ultimately, the alignment of these elements emphasizes the importance of connected worker technologies in contemporary industrial landscapes.
Connected Worker Market Definition
A connected worker is an individual who employs digital technologies and tools to optimize communication, collaboration, and productivity in a work environment. This idea typically includes the use of intelligent devices, Internet of Things (IoT) systems, and data analysis to enhance operational effectiveness and safety.
In the contemporary industrial environment, the role of the Connected Worker is vital for boosting productivity, safety, and teamwork. Utilizing cutting-edge technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), wearable devices, and mobile platforms, employees can access essential information in real time. This access empowers them to make informed decisions and perform their tasks more efficiently. Enhanced connectivity facilitates smooth communication between team members, minimizes downtime, and improves responsiveness to new challenges. Additionally, through the use of data analytics, companies can recognize patterns, optimize workflows, and adhere to safety standards, all of which promote operational excellence. Prioritizing Connected Workers not only enhances individual capabilities but also strengthens the organization’s agility and resilience.
Connected Worker Market Segmental Analysis:

Insights On Type
Software
Software is expected to dominate the Global Connected Worker Market due to the increasing reliance on digital solutions to enhance workforce efficiency and collaboration. With businesses adopting advanced technologies, software tools that facilitate communication, data management, and real-time analytics are becoming essential. The rise of cloud-based platforms and mobile applications enables workers to connect and share information seamlessly, thus optimizing operations and improving productivity. Moreover, the integration of AI and machine learning in software solutions is significantly enhancing decision-making capabilities and predictive analytics, making them critical for organizations aiming to stay competitive in the rapidly changing market landscape.
Hardware
Hardware plays a crucial role in the Global Connected Worker Market by providing the necessary physical devices that facilitate connectivity and interaction within the workforce. Devices such as wearables, sensors, and mobile devices are essential for real-time data collection and communication in various industries. However, although hardware is integral for implementation, its growth is often dependent on the advancements in software solutions that can fully utilize the capabilities of these devices. Consequently, while hardware is vital, it often takes a supportive role in comparison to the leading impact of software solutions driving market demand.
Services
Services associated with the Global Connected Worker Market encompass a range of offerings, including consulting, maintenance, and support. They are instrumental in ensuring that the hardware and software solutions are effectively integrated and utilized across organizations. While the demand for services continues to grow as companies seek to maximize the return on investment from their connected worker initiatives, they typically follow the implementation of hardware and software technologies. The emphasis on seamless user experiences and ongoing support highlights the importance of services, yet they often remain a secondary focus in relation to the dominating influence of software solutions.
Insights On Technology
Cellular
Cellular technology is poised to dominate the Global Connected Worker Market due to its superior range, mobility, and robust data handling capabilities. With the increasing need for real-time data exchange and communication in various industries, Cellular offers a reliable and wide-reaching connection that can effortlessly integrate into the existing infrastructure. Technologies such as 4G and upcoming 5G ensure high-speed data transfer and low latency, which are critical for connected worker applications in sectors like manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare. The growing number of IoT devices and the push for smart factories further amplify Cellular’s relevance, making it the leading choice for enterprises seeking efficient and scalable connectivity solutions.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth technology is primarily favored for short-range, low-power applications, especially in environments where devices need to maintain connectivity in close proximity. It serves an essential role in ensuring seamless communication between wearables and personal devices in the connected worker ecosystem. Bluetooth’s ease of integration and low energy consumption appeal to industries looking for efficient solutions without significant infrastructure changes. However, its limited range might restrict its application in larger-scale operations, making it less suitable compared to other technologies like Cellular for broader connected purposes.
RFID
RFID technology is crucial in asset tracking and inventory management, offering businesses significant efficiency gains. Its inherent ability to quickly and accurately identify and track items without needing a direct line of sight is beneficial in warehouses, retail, and manufacturing. RFID systems can streamline operations, reduce human error, and improve inventory control. However, RFID's limitations in range and the complexity of tags can hinder its application in environments demanding extensive communication, thereby making its role more specialized within the broader connected worker framework.
Zigbee
Zigbee technology is known for its low-power and cost-effective wireless communication, particularly in home automation and industrial control systems. It excels in areas requiring multiple devices to communicate within a mesh network, making it suitable for smart building applications and energy management systems. However, its limited range compared to Cellular and Wi-Fi technologies restricts its viability in larger industrial settings, where broader coverage and higher data throughput are necessary. Zigbee's niche applications in localized environments are still valuable, but its use may be overshadowed by other connectivity technologies.
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi technology remains a dominant force in providing high-speed wireless internet access within local environments. Its ability to support numerous devices simultaneously and offer significant bandwidth makes it popular in office settings and large industrial facilities. As businesses adapt to more connected workers, Wi-Fi solutions enable seamless data sharing and collaboration through various connected tools. Nevertheless, the need for infrastructure setup and potential interference issues in high-density areas can deter its use in environments where mobility across locations is crucial.
LPWAN
LPWAN technology focuses on providing low-power, wide-area network solutions that are perfect for IoT applications where devices transmit small amounts of data over long distances. This makes it particularly relevant for industries such as agriculture or remote monitoring, where connected workers need reliable communication across vast areas. While LPWAN excels in battery longevity and covering extensive geographic regions, it generally offers lower data transfer rates, making it less suitable for high-demand applications that require real-time data exchange compared to Cellular technology.
WFAN
WFAN (Wireless Fabric Area Network) technology is optimized for connectivity in smart buildings, enhancing communication among various devices. This technology is particularly useful in enabling efficient operations, such as lighting and energy management, contributing to the overall functionality of connected workspaces. Despite its potential for improving operational efficiency, WFAN's existence is often tied closely to its specific applications and may not stand as a primary choice against the robustness of Cellular connectivity for widespread deployments, particularly in industrial settings requiring more flexible and reliable communication solutions.
Insights On Deployment
Cloud
The Cloud deployment method is expected to dominate the Global Connected Worker Market due to its ability to provide scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Organizations are increasingly looking for solutions that can easily adapt to changing business needs, and cloud-based systems allow for rapid deployment and updates without necessitating significant upfront investments in infrastructure. The ability to access data and applications remotely enhances collaboration and productivity among connected workers, making it an attractive choice for businesses seeking to improve operational efficiencies. Additionally, security and compliance features offered by cloud service providers continue to advance, alleviating concerns that companies may have about data safety.
On-premises
The On-premises deployment option caters to organizations that prefer maintaining full control over their data and systems. This method appeals to industries with stringent regulatory requirements or concerns about data privacy, as it allows for localized data management and processing. While this approach can entail higher initial costs and longer implementation times, some enterprises still opt for it to mitigate risks associated with third-party data breaches. The visibility and control over the entire operational environment can be vital for certain sectors, providing assurance to companies focusing on compliance and data security.
Insights On Organisation Size
Large Enterprise
Large enterprises are expected to dominate the Global Connected Worker Market due to their significant investment capacity in technology and infrastructure. These organizations typically have the resources to implement and integrate advanced connected worker solutions, such as IoT devices, training programs, and management tools. The complexity and scale of their operations necessitate a comprehensive adoption of connected worker technologies to enhance productivity, efficiency, and safety. Furthermore, large enterprises often benefit from economies of scale, allowing them to leverage cost advantages when implementing new technologies. As a result, they are more likely to lead the market with sophisticated connected worker strategies and solutions.
SMEs
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) face various challenges when it comes to integrating connected worker technologies. One of the most significant barriers is the limited financial resources that constrain their ability to invest in new solutions. Although SMEs recognize the benefits of connected worker systems, they often prioritize immediate operational needs over long-term technological advancements. Consequently, the adoption rate within this remains lower compared to larger organizations, slowing their contribution to the overall market growth. However, with increasing affordable solutions and support from government initiatives targeting SMEs, there is potential for gradual growth in this area.
Insights On End User
Manufacturing
The manufacturing sector is anticipated to dominate the Global Connected Worker Market due to its rapid adoption of digital technologies and automation. As manufacturers increasingly integrate IoT solutions, wearable devices, and real-time data analytics into their operations, the efficiency and productivity of workers are significantly enhanced. Moreover, this industry prioritizes health and safety standards, driving the need for connected solutions to monitor worker conditions and streamline communication. As the competition intensifies and operational excellence becomes crucial, manufacturing is likely to continue leading the connected worker market, showcasing the potential for growth and innovation.
Building and Construction
The building and construction industry is embracing connected worker technologies primarily to improve project management and worker safety. Implementing wearables and mobile devices allows for better real-time communication on job sites, reducing risks associated with construction work. Furthermore, it aids in tracking productivity and project timelines, which is vital in a sector often challenged by delays and cost overruns. The push towards smart buildings also creates a demand for coordinated efforts among workers, thereby fostering the growth of connected solutions in this sector.
Mining
In the mining sector, connected worker technologies are gaining traction as companies seek to enhance safety and operational efficiency. Deploying IoT-enabled devices allows for monitoring environmental conditions and worker health, reducing the risks associated with hazardous conditions. Real-time analytics facilitate on-site decision-making, optimizing resource utilization and improving overall productivity. As the industry faces increasing pressure to maintain safety standards and operational agility, the implementation of connected worker solutions is likely to play a pivotal role in transforming mining operations.
Oil and Gas
The oil and gas industry has been slow in adopting connected worker solutions, but this landscape is changing as firms recognize the importance of enhancing safety and efficiency. By leveraging digital technologies, companies can monitor and manage worker safety in remote locations, minimizing risks associated with hazardous environments. Additionally, real-time data collection allows for improved collaboration among teams, which directly impacts operational efficiency. As the industry begins to embrace these innovations to get ahead in a competitive landscape, the connected worker market in oil and gas is expected to see gradual growth.
Utilities
The utilities sector is starting to recognize the potential of connected worker technologies to address the complexities of modern utility management. One major benefit is the ability to monitor field worker activities and ensure compliance with regulations and safety standards. Utilizing wearable devices and mobile applications facilitates effective communication, improving incident response times. As utilities strive to modernize their infrastructures and improve service reliability in conjunction with renewable energy adoption, the integration of connected worker solutions is likely to become increasingly significant in this.
Telecom
The telecom industry, while not the leader, is leveraging connected worker technologies to improve operations and enhance customer service. As companies expand their networks and deploy new technologies, there is a growing need for real-time collaboration and communication among workers. Mobile applications that enable remote assistance and task management enhance efficiency at service sites. Moreover, the need for seamless implementation and maintenance of telecom infrastructure creates opportunities for connected solutions to reduce downtime and improve service delivery.
Home Service
The home service sector is witnessing a gradual increase in the adoption of connected worker technologies as companies seek to enhance customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Service technicians can utilize mobile applications to streamline scheduling, management, and communication, resulting in quicker response times for clients. Additionally, tools that aid in remote assessments reduce the need for in-person visits. The growing trend of smart home devices further incentivizes technicians to adopt connected solutions, thereby driving incremental growth in this space.
Global Connected Worker Market Regional Insights:
North America
North America is expected to dominate the Global Connected Worker market primarily due to its advanced technological infrastructure, high adoption rates of innovative technologies, and a significant presence of major industry players. The region benefits from substantial investments in IoT, AI, and cloud computing, which are essential components of the Connected Worker ecosystem. Additionally, companies in North America are actively seeking to enhance workforce productivity and safety, driving the demand for connected worker solutions. Regulatory support and a growing emphasis on digital transformation initiatives across various sectors further solidify North America's leading position in this market.
Latin America
Latin America is gradually emerging in the Global Connected Worker market, driven by increasing digital transformation initiatives across several industries. While adoption rates are lower compared to North America, countries like Brazil and Mexico are focusing on integrating connected worker solutions to improve operational efficiency and workforce safety. Government initiatives promoting digitization and investments from both domestic and international firms are contributing to this market's growth. However, challenges such as infrastructure limitations and economic instability may hinder faster adoption rates in some parts of the region.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific is experiencing significant growth in the Global Connected Worker market, fueled by rapid industrialization, particularly in countries like China, India, and Japan. The rising demand for automation and intelligent connected devices in manufacturing and construction sectors is propelling the adoption of connected worker solutions. Additionally, strong government support for smart factories and initiatives aimed at enhancing employee productivity and safety are expected to further drive growth. However, varying degrees of technological maturity across different countries in the region could impact the overall market performance.
Europe
Europe holds a considerable share in the Global Connected Worker market, thanks to stringent regulatory standards focused on workplace safety, as well as strong initiatives towards sustainability and digital transformation. The European Union's focus on smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 significantly bolsters the demand for connected worker solutions. Countries like Germany and the UK are leading the charge with widespread adoption of IoT and advanced technologies in various sectors. However, challenges related to varying regulatory frameworks and data privacy concerns may pose hurdles for market growth in certain areas.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region is still in the early stages of adopting connected worker solutions, but there is a growing interest driven by factors such as economic diversification and increased investment in technology infrastructure. Industries such as oil and gas, construction, and mining are beginning to recognize the benefits of connected worker implementations for enhancing safety and efficiency. Nonetheless, hurdles including insufficient technological infrastructure in some areas and a lack of skilled workforce are challenges that could impede more rapid market growth in this region.
Connected Worker Competitive Landscape:
Prominent entities in the Global Connected Worker sector, including technology vendors and service integrators, are at the forefront of driving innovation by offering sophisticated solutions and platforms that improve communication and productivity for both remote and on-site personnel. Their partnerships facilitate the creation of IoT applications and wearable devices, significantly enhancing workforce efficiency across various industries.
Prominent participants in the Connected Worker Market comprise Microsoft Corporation, IBM Corporation, Cisco Systems, Inc., Honeywell International Inc., PTC Inc., SAP SE, Siemens AG, Augmentir, Inc., AT&T Inc., Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., ABB Ltd., Rockwell Automation, Inc., Accenture PLC, General Electric Company, and Oracle Corporation.
Global Connected Worker COVID-19 Impact and Market Status:
The Covid-19 pandemic markedly expedited the integration of remote work technologies, propelling the expansion of the Global Connected Worker market as organizations pursued novel strategies to improve collaboration and boost productivity.
The COVID-19 pandemic has greatly accelerated the expansion of the Connected Worker sector as organizations transitioned to remote work and sought innovative methods to sustain productivity and collaboration. With an increased emphasis on safety, operational continuity, and efficiency, enterprises began integrating technologies such as augmented reality (AR), wearable technology, and IoT applications to facilitate remote support and training initiatives. Effective communication tools became crucial, enabling seamless real-time interactions between on-site and remote employees. The demand for optimized processes and advanced data analytics further fueled investment in connected worker solutions, which play a pivotal role in monitoring workforce health and refining operational workflows. Moreover, sectors including manufacturing, construction, and logistics have acknowledged the importance of connected worker technologies for managing compliance and ensuring a smooth flow of information amid disruptions. Ultimately, the pandemic has transformed the environment, positioning connected worker solutions as essential components of contemporary business strategies.
Latest Trends and Innovation in The Global Connected Worker Market:
- In January 2023, Siemens announced an expansion of its digital offerings for connected workers with the introduction of new features in its Xcelerator portfolio, which enhances collaboration and productivity in manufacturing environments through improved data insights.
- In March 2023, Honeywell acquired the software company Intellinum, enhancing Honeywell’s Connected Worker solutions by integrating advanced real-time data analytics and artificial intelligence capabilities to improve workplace safety and operational efficiency.
- In April 2023, PTC launched new augmented reality (AR) tools within its Vuforia platform, aimed at connected workers, enabling manufacturers to create more immersive training experiences and enhance on-the-job guidance for frontline employees.
- In July 2023, IBM announced a partnership with ServiceNow to develop AI-driven solutions that empower connected workers through improved incident response and workflow automation, significantly streamlining operational processes across industries.
- In September 2023, Microsoft unveiled further development of its Mesh platform for mixed reality, allowing connected workers to collaborate more effectively across remote locations through holographic interactions, aiming to enhance virtual teamwork and project management.
- In October 2023, Qualcomm launched its new XR platform, specifically designed for connected worker applications in manufacturing and logistics, focusing on the integration of IoT and AI to provide real-time operational insights and improve decision-making processes on the floor.
Connected Worker Market Growth Factors:
The expansion of the Connected Worker Market is fueled by the necessity for increased operational effectiveness, ened safety measures, and immediate access to data across various sectors.
The Connected Worker Market is witnessing remarkable expansion, influenced by several pivotal factors. Foremost among these is the widespread integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, including the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing, which collectively boost operational productivity and improve worker connectivity. Additionally, there is an escalating need for real-time data analysis, empowering organizations to swiftly make informed choices that enhance efficiency and responsiveness across diverse fields such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics.
Another significant driver of this market is the demand for ened worker safety and enhanced training, especially in high-risk environments; connected devices enable continuous monitoring and support for employees. The ongoing digital transformation throughout various industries compels businesses to adopt connected worker solutions, leading to more streamlined operations and improved collaboration. The shift towards remote and hybrid work arrangements, significantly accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, has further increased the dependency on digital tools and platforms, thereby fueling market growth.
Moreover, governmental initiatives and investments aimed at improving digital infrastructure and promoting smart technologies are also favorably impacting market development. Together, these elements are fostering a dynamic landscape for Connected Worker solutions, setting the stage for enduring growth in the near future.
Connected Worker Market Restaining Factors:
Major limiting factors in the Connected Worker Market encompass issues related to data security and privacy, significant costs associated with implementation, and the risk of technological obsolescence.
The Connected Worker Market encounters multiple challenges that could impede its development. A primary hurdle is the substantial upfront capital necessary for the adoption of cutting-edge technologies, such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices, wearable technology, and unified software solutions. This financial burden can particularly affect small to medium-sized businesses that may not have sufficient funds. Moreover, ongoing concerns over cybersecurity and data privacy arise, as the proliferation of interconnected devices ens the potential risk of cyber threats and data breaches, which may dissuade some firms from fully adopting these innovative solutions. There is also a reluctance to change among both employees and management, which can obstruct the transition from conventional operational practices to modern connected worker technologies. In addition, the varied regulatory landscape across different geographical regions presents challenges, complicating compliance efforts for multinational corporations. Nonetheless, the growing awareness of the advantages tied to connected worker solutions—such as increased productivity, enhanced safety protocols, and optimized operations—fuels innovation and promotes a burgeoning market. This determination to address existing obstacles indicates a promising outlook for the Connected Worker Market, as organizations increasingly focus on digital transformation to enhance their competitive edge.
Key Segments of the Connected Worker Market
By Type
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
By Technology
- Cellular
- Bluetooth
- RFID
- Zigbee
- Wi-Fi
- LPWAN
- WFAN
By Deployment
- Cloud
- On-premises
By Organisation Size
- Large Enterprise
- SMEs
By End User
- Manufacturing
- Building and Construction
- Mining
- Oil and Gas
- Utilities
- Telecom
- Home Service
Regional Overview
North America
- US
- Canada
- Mexico
Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K
- Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Rest of Asia Pacific
Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of Middle East and Africa
Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America

