Market Analysis and Insights
The market for cyber security insurance is predicted to grow at a CAGR of around 18.08% over the aforementioned forecast period, the market was valued at USD 9.10 billion in 2021 and would reach USD 61.05 billion in 2031.
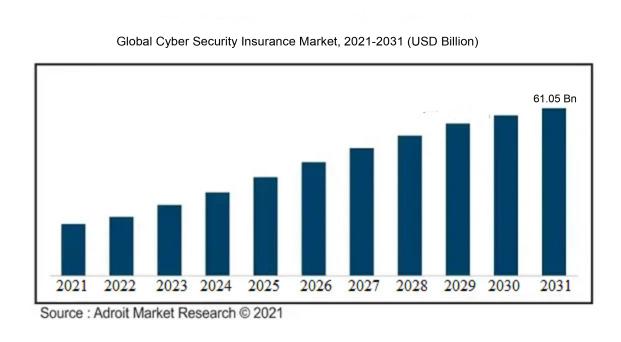
As a result of technological developments, small, medium, and large-scale businesses are increasingly using cybersecurity insurance. Additionally, as media coverage of commercial assaults increased, more businesses expressed a desire to get cyber insurance. With tougher underwriting and risk management standards, cyber dangers are being more rigorously monitored.
Cyber Security Insurance Market Scope:
| Metrics | Details |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Historic Data | 2018-2022 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2031 |
| Study Period | 2018-2031 |
| Forecast Unit | Value (USD) |
| Revenue forecast in 2031 | USD 61.05 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 18.08% during 2021-2031 |
| Segment Covered | by Component ,Type, by Coverage ,by Organization Size ,End-user Industry ,By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America, Middle East and Africa |
| Key Players Profiled | Security Scorecard, BitSight, Prevalent, RedSeal, Zurich Insurance, Cyber Indemnity Solutions, Microsoft, Check Point, Cisco, Lloyd’s of London, Axis Capital, UpGuard, AttackIQ, Broadcom, Accenture, Founder Shield, AIG, Arthur, CyberArk, CYE, SecurIT360, Travelers Insurance, CNA Financial, Fairfax Financial, Cylance, FireEye, Liberty Mutual, and others. |
Market Definition
Cybersecurity insurance is a type of insurance designed to protect people and organizations against the financial losses and liabilities brought on by cyber incidents and data breaches. Cybersecurity insurance is sometimes referred to as cyber insurance or cyber risk insurance. It offers protection against a range of expenses and losses brought on by data breaches, cyberattacks, and other cybersecurity incidents.
A wide range of risks are covered by cyber insurance plans and enterprises, and insurers frequently disagree on the kind of loss occurrences that are covered. Cyber events include features that make it difficult to create comprehensive rules, such as a limited loss history, the inaccuracy of previous data in predicting future events, and the potential for a large-scale assault with losses that are strongly connected across businesses and industries.
In addition, insurers are still developing specific and accurate criteria for cyberattacks as well as the effects of cutting-edge technology like the Internet of Things. If significant cyberattacks occur without clear threats and a knowledge of how they influence insurers, cyber insurance coverage may be inadequate and expose businesses to significant risk.
Key Market Segmentation

Insights on Type
The Standalone Segment Valued for the Highest Share
Media liability insurance, which covers claims of libel or slander, invasion of privacy, and other wrongdoings, is available as a standalone policy. The Standalone insurance also provides coverage for additional property exposures such as business interruption, data loss and destruction, and money transfer loss. An organization's risk exposure is reduced by compensating the expenses connected to recovering from a security breach involving computers or a similar incident. In order to secure sensitive data in the cloud, businesses are being forced by current cyber security to use more complicated insurance arrangements. The market for cyber insurance is expanding as a result of all of these factors.
Insights on End User
The BFSI Segment Accounted for the Highest Share
The BFSI industry is one of the key infrastructure areas that regularly experiences data breaches and cyberattacks due to its large clientele and the sensitive financial data that is at danger. Since the financial sector has an operational model that is extremely profitable, boasts spectacular earnings, and has the added benefit of having relatively little risk and detectability, cybercriminals are using a wide variety of evil cyberattacks to paralyze it.
Insights on Region
The North American Region Accounted for the Highest Share
It is believed that the United States is the largest market for cybersecurity insurance. The nation's strong market share is also attributed to the existence of a considerable number of significant businesses there. Cyberattacks are on the rise and have reached an all-time high in the United States due to the country's quickly growing network of linked gadgets. Customers use public clouds in the US, and many of their mobile applications come pre-loaded with personal data for the ease of banking, shopping, communicating, etc.
Key Company Profiles
Some key players in the global market are Security Scorecard, BitSight, Prevalent, RedSeal, Zurich Insurance, Cyber Indemnity Solutions, Microsoft, Check Point, Cisco, Lloyd’s of London, Axis Capital, UpGuard, AttackIQ, Broadcom, Accenture, Founder Shield, AIG, Arthur, CyberArk, CYE, SecurIT360, Travelers Insurance, CNA Financial, Fairfax Financial, Cylance, FireEye, Liberty Mutual, and others.
COVID-19 Impact and Market Status
Cybercriminals now have new options thanks to the epidemic as businesses extended their digital presence and quickly embraced remote working practices.
Cyberattacks such as phishing schemes, ransomware events, and data breaches increased as a result of this. The demand for cyber security insurance has been impacted by the rising frequency and sophistication of cyber assaults.
In light of the ened cyber dangers that organizations were facing, the pandemic highlighted the crucial significance of strong cyber security measures. Organizations have been prompted by this increased awareness to reevaluate their exposure to cyber risk and look for cyber security insurance coverage to guard against potential financial losses and reputational harm.
The remote work trend and the quick uptake of digital solutions have altered organizations’ risk profiles and created new risks. In order to effectively assess cyber risk exposure and choose the right insurance coverage, insurers have to adjust to these changing risk landscapes and reassess their underwriting standards.
Latest Trends
1. In order to evaluate cyber risk and estimate possible financial effects, insurers are using advanced analytics and data-driven methodologies. In order to better understand and precisely price cyber insurance policies, they are utilizing models and algorithms to analyze an organization's cyber security posture, threat information, and historical data.
2. To improve their offering and give customers value-added services, insurers are creating relationships with cybersecurity firms, technology suppliers, and incident response providers. Through these agreements, insurers may access cutting-edge security solutions, benefit from specialized knowledge, and speed up incident response and recovery.
3. Insurance companies are providing specialized coverage suited to certain sectors or company requirements as cyber hazards become more varied and complicated. These plans provide coverage that is in line with the particular cyber security difficulties encountered by organizations in certain areas, which include healthcare, banking, and manufacturing. They also handle the distinctive cyber risk profiles and regulatory needs of various industry sectors.
4. Incident response services are a growing aspect of what insurers provide in their cyber security insurance plans. To assist organizations in successfully responding to and recovering from cyber events, these services may include access to cyber security professionals, forensic investigators, public relations specialists, and legal counsel.
Significant Growth Factors
The need for cyber security insurance is being driven by the increase in the quantity and complexity of cyber assaults, including data breaches, ransomware, and social engineering.
The necessity for financial protection against possible losses and liabilities brought on by cyber catastrophes is becoming more and more apparent to organizations.
The adoption of data protection legislation like the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and the CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) has increased the importance of data security and privacy. The need for cyber security insurance as a risk management tool is fueled by the fact that compliance with these standards frequently involves specifications for cyber security measures and incident response plans.
The need for cyber security insurance is being fueled by the continuously changing cyber risk landscape, which is seeing new threats and vulnerabilities emerge on a daily basis. Organizations are more vulnerable to cyber hazards as they adopt new technologies like cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence (AI), thus insurance coverage is essential.
Restraining Factors
Even while awareness of cyber dangers and the benefits of cyber security insurance is growing, many organizations still only have a basic grasp of them.
Lower adoption rates may result from people underestimating the possible financial effects of a cyber disaster or from people not knowing about the available insurance solutions.
Some firms, especially smaller ones or those with tighter resources, may be put off by the expense of cyber security insurance.
Premiums may be expensive, especially for businesses with weak cyber security defences. The difficulty is in finding a balance between insurance costs and the possible financial effects of a cyber catastrophe.
Assessing cyber risk and underwriting cyber security insurance policies can be complex. Insurers need accurate and up-to-date information about an organization's cyber security practices, incident response capabilities, and risk management procedures. The lack of standardized risk assessment methodologies and the evolving nature of cyber threats present challenges in accurately pricing policies.
Recent Developments in the Global Cyber Security Insurance Market: A Snapshot
• Launch of CloudCover CyberCell, a cybersecurity "rent-a-captive" insurance programme, in February 2023 thanks to a partnership between CloudCover Re and insurance brokerage Hylant Global Captive Solutions (Hylant). The programme enables users to manageably fund self-insured cyber risks and is accessible to organizations, affinity groups, and major businesses. This lowers the potential liability of cyberattacks and makes it possible for businesses to generate larger amounts of cash since they may offer cyber insurance at a lower price and with more coverage.
• In November 2022, RCCS (Ridge Canada Cyber Solutions Inc.), one of the top leading general insurance firms, and Agilicus, a cybersecurity firm, partnered together to assist Canadian small to midsize businesses (SMBs) in becoming eligible for and obtaining cybersecurity insurance.
Key Segments of the Cyber Security Insurance Market
Component Overview
• Solution
• Services
Type Overview
• Standalone
• Packaged
Coverage Overview
• Data Breach
• Cyber Liability
Organization Size Overview
• Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
• Large Enterprises
End-User Industry Overview
• Healthcare
• Retail
• BFSI
• IT and Telecom
• Manufacturing
Regional Overview
North America
• U.S
• Canada
Europe
• Germany
• France
• UK
• Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
• China
• India
• Japan
• Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
• Mexico
• Brazil
• Rest of South America

