Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market Analysis and Insights:
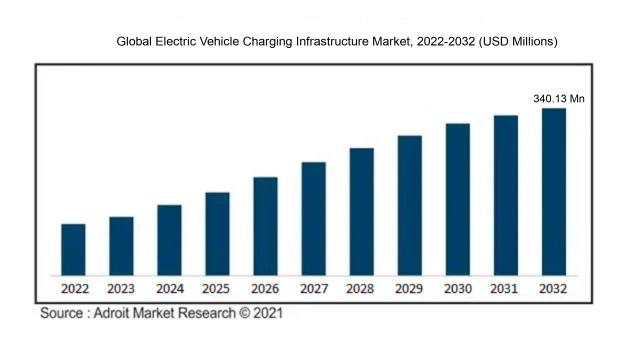
The market for Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure was estimated to be worth USD 80.29 million in 2022, and from 2023 to 2032, it is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 14.93%, with an expected value of USD 340.13 million in 2032.
The surge in the Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market is driven by various factors. One key catalyst is the global pursuit of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and addressing climate change, resulting in a surge in electric vehicle adoption and subsequently creating a demand for charging infrastructure. Moreover, governmental backing in the form of subsidies, tax breaks, and favorable policies has been influential in encouraging the installation of charging stations. Advances in battery technology and the proliferation of fast-charging solutions have alleviated concerns about range anxiety, making electric vehicles more attractive to consumers. Additionally, the increasing collaborations and partnerships between automakers, energy firms, and charging equipment manufacturers have accelerated the deployment of charging infrastructure. Lastly, the transition to renewable energy sources and the incorporation of smart grid technologies have made it more viable and sustainable to expand the electric vehicle charging network. Collectively, these factors paint a promising picture for the Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market, propelling its growth trajectory in the foreseeable future.
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market Definition
An electric vehicle charging infrastructure encompasses the array of charging stations and auxiliary facilities that facilitate the recharging of electric vehicles (EVs). It serves as a pivotal component in mitigating the concerns surrounding the limited range of EVs, thereby fostering the extensive acceptance of electric mobility.
The infrastructure for charging Electric Vehicles (EVs) plays a pivotal role in enabling the widespread acceptance of electric vehicles and moving towards a more sustainable future. This infrastructure is crucial in alleviating concerns related to limited driving range and lengthy charging periods by offering convenient and easily accessible charging solutions for EV users. A well-established network of charging stations ensures that EV drivers feel reassured and have the convenience of charging their vehicles while on the move, thereby eradicating any worries about running out of power mid-journey. Furthermore, it motivates people to make the transition from conventional fossil fuel-operated vehicles to electric vehicles, thereby diminishing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting cleaner air quality. A comprehensive and dependable network for charging EVs is essential for encouraging the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and attaining the objectives of fostering a sustainable and decarbonized transportation industry.
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market Segmental Analysis:

Insights On Offering
EV Charging Solutions
EV Charging Solutions are expected to dominate the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market. With the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) worldwide, there is a growing need for efficient and convenient charging solutions. EV Charging Solutions encompass a range of hardware and software components that provide charging stations and related infrastructure. These solutions enable fast and reliable charging, offering features such as high-power charging, wireless charging, and smart charging management systems. As governments and industries push for widespread EV adoption, the demand for EV Charging Solutions is set to soar, making it the dominant part in the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market.
EV Charging Services
While EV Charging Solutions are expected to dominate the market, EV Charging Services also play a significant role in the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market. EV Charging Services refer to the various services offered to EV owners, such as subscription plans, payment processes, network connectivity, and maintenance support. These services are crucial in providing a seamless and convenient charging experience for EV users. Although not as prominent as EV Charging Solutions, EV Charging Services are an integral part of the overall charging infrastructure. As the market continues to evolve, EV Charging Services will contribute to the overall growth and development of the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market.
Insights On Portability
Portable/Mobile EV Chargers
Portable/Mobile EV Chargers are expected to dominate the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure market. With the rising popularity of electric vehicles and the need for convenient charging solutions, portable/mobile EV chargers offer flexibility and ease of use. These chargers can be easily transported and used in various locations, such as homes, workplaces, and public spaces. Moreover, with advancements in technology, portable/mobile EV chargers are becoming more efficient and faster in charging electric vehicles. This part is expected to witness significant growth in the coming years due to the increasing adoption of electric vehicles globally.
Stationary EV Chargers
While portable/mobile EV chargers are expected to dominate the market, stationary EV chargers also hold significance in the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure market. Stationary EV chargers are primarily used in fixed locations such as charging stations, parking lots, and commercial buildings. These chargers usually provide higher power output and faster charging times compared to their portable counterparts. Stationary EV chargers are crucial for creating a robust charging infrastructure, especially in areas with high electric vehicle usage, such as public charging stations and fleet charging facilities. Although not projected to dominate the market, stationary EV chargers will continue to play a vital role in supporting the charging needs of electric vehicle owners in various settings.
Insights On Charging Point
DC Charger
The DC Charger is expected to dominate the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market. DC chargers are known for their fast charging capabilities, allowing electric vehicles to charge at a higher voltage and current. This makes them highly desirable for electric vehicle owners who are looking for quick and efficient charging solutions. Additionally, DC chargers are commonly used in public charging stations, making them more accessible and convenient for users who are on the go. As the demand for electric vehicles continues to rise, the need for fast and efficient charging infrastructure will also increase, cementing the DC charger part's dominance in the market.
AC Charger
While AC chargers are also an essential sector of the electric vehicle charging infrastructure, they are not expected to dominate the market compared to DC chargers. AC chargers operate at a lower voltage and current, resulting in slower charging times compared to their DC counterparts. However, AC chargers are typically used for charging at home or in work environments, where longer charging times are acceptable. This part will continue to play a significant role in providing charging solutions for those who primarily charge their vehicles in residential or office settings.
Insights On Mounting Type
Wall Mounted Charger
Wall Mounted Chargers are expected to dominate the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market. These chargers are highly convenient and space-saving, making them a popular choice for residential and commercial settings. With their ability to be installed on walls, they offer flexibility and ease of use, allowing vehicle owners to charge their electric vehicles conveniently at home or in parking facilities. Furthermore, advancements in technology have led to the development of fast-charging wall mounted chargers, reducing charging time and increasing the adoption of electric vehicles. As a result, the demand for wall mounted chargers is projected to increase significantly, making them the dominating part in the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market.
Pedestal Mounted Charger
Although Wall Mounted Chargers are expected to dominate the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market, Pedestal Mounted Chargers still play a crucial role in the market. Pedestal Mounted Chargers are typically found in public areas such as parking lots, shopping centers, and roadside stations. They offer reliable charging solutions for electric vehicle users who do not have access to Wall Mounted Chargers. Additionally, Pedestal Mounted Chargers often have multiple charging ports, allowing multiple vehicles to charge simultaneously, making them ideal for high-traffic areas. While they may not be as prevalent as Wall Mounted Chargers, Pedestal Mounted Chargers still serve an essential function in providing accessible charging options to electric vehicle users in public spaces.
Insights On Standard
Megawatt Charging System (MCS)
The Megawatt Charging System (MCS) is expected to dominate the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market. With the increasing demand for fast charging solutions, especially for commercial and industrial applications, the MCS provides a high-power charging option. It offers rapid charging capabilities, enabling electric vehicles to achieve longer driving ranges in a shorter amount of time. This makes it highly suitable for fleet operators, logistics companies, and other industries that require fast and efficient charging solutions. The MCS is anticipated to play a crucial role in the growth of the electric vehicle charging infrastructure market.
Combined Charging System (CCS)
While the Megawatt Charging System is expected to dominate the market, the Combined Charging System (CCS) holds significant potential as well. The CCS combines the ability to deliver both AC and DC charging, making it compatible with a wide range of electric vehicles. This flexibility allows for seamless integration with existing charging infrastructure, promoting interoperability and ease of use. As the adoption of electric vehicles continues to grow, the CCS is likely to see increased demand, especially in residential and urban areas where diverse charging needs exist.
Others
Although the Megawatt Charging System (MCS) is expected to dominate the market, it is essential to consider the potential of other parts in the electric vehicle charging infrastructure market. This includes emerging technologies and charging solutions that cater to specific niches or requirements. These Others category incorporates innovative charging technologies such as wireless charging, ultra-fast charging, and solar-powered charging stations. While currently not dominating the market, these alternative charging solutions hold promise for future growth and may find niche applications in specific regions or specialized needs. Their impact on the global market cannot be ignored, as they contribute to the overall development and evolution of electric vehicle charging infrastructure.
Insights On Phase
Three Phase
Three Phase charging infrastructure is expected to dominate the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure market. This is because Three Phase charging systems offer higher power output, enabling faster charging times for electric vehicles. With growing demand for electric vehicles and the need for efficient charging solutions, Three Phase infrastructure provides a competitive advantage by reducing charging time and improving convenience for EV users. Additionally, Three Phase charging systems allow for more balanced power distribution and better grid integration, making them a preferred choice for commercial and public charging stations.
Single Phase
Single Phase charging infrastructure, while not expected to dominate the market, still holds significance in certain contexts. Single Phase charging systems are commonly used for residential charging applications, catering to individual EV owners who primarily charge their vehicles at home. These charging systems are comparatively less powerful than Three Phase infrastructure, resulting in longer charging times. However, for individuals with limited charging requirements or access to slower charging speeds, Single Phase infrastructure remains a viable option. Furthermore, with the increasing adoption of electric vehicles in residential areas, Single Phase infrastructure plays a crucial role in supporting home charging needs.
Insights On Charging Level
Level 3
The Level 3 is expected to dominate the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market. Level 3 charging, also known as DC fast charging, provides the fastest charging option for electric vehicles. With its ability to deliver high power levels, Level 3 charging significantly reduces the charging time compared to Level 1 and Level 2 charging. This makes Level 3 charging more convenient for electric vehicle users, especially those in need of a quick charge, such as during long trips. As a result, the demand for Level 3 charging infrastructure is expected to grow rapidly, leading to its domination in the market.
Level 1
Level 1 charging, which uses a standard household outlet, is not expected to dominate the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market. While Level 1 charging is the most basic and widely available form of electric vehicle charging, it has limitations in terms of charging speed. Level 1 chargers typically provide a low charging power, resulting in longer charging times compared to Level 2 and Level 3 chargers. However, Level 1 charging is still relevant for residential charging needs or in locations where fast charging options are not required.
Level 2
Level 2 charging is another sector of the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market. It offers faster charging compared to Level 1 charging and is commonly used for residential charging stations, workplace charging, and public charging stations. Although Level 2 charging provides faster charging speeds than Level 1, it is not expected to dominate the market as Level 3 charging offers even faster charging times. Nonetheless, Level 2 charging infrastructure is crucial for supporting the growing number of electric vehicles and meeting the needs of daily commuters or overnight charging.
Insights On Application
Fleets
Fleets are expected to dominate the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market. The increasing adoption of electric vehicles in fleet operations, including government, taxi, and ride-hailing services, is driving the demand for charging infrastructure. Fleets require charging infrastructure for their operations, and with the growing focus on sustainability and reducing emissions, more fleet operators are transitioning to electric vehicles. This shift is expected to drive the demand for charging infrastructure specifically tailored for fleet operations, resulting in the domination of this part in the global market.
Residential
The residential application of the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market is anticipated to play a significant role but not dominate the market. While many electric vehicle owners prefer to charge their vehicles at home, the availability of alternative charging options, such as workplace charging and public charging stations, may limit the dominance of the residential part. Additionally, the growth of multi-unit dwellings and the need for charging infrastructure in such settings may further impact the dominance of the residential part.
Workplace
The workplace application is expected to be an important sector of the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market. With the increasing number of companies implementing sustainable practices and encouraging their employees to adopt electric vehicles, the demand for workplace charging infrastructure is growing. However, it is unlikely to dominate the overall market due to the presence of other parts like fleets, retail, and roadside stations. Nevertheless, workplace charging infrastructure will remain a significant player in the market, supporting the charging needs of employees and promoting the adoption of electric vehicles.
Retail
Retail charging infrastructure is expected to have a notable presence in the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market. Retail establishments, including shopping malls, supermarkets, and convenience stores, can attract electric vehicle owners by offering charging facilities. While retail charging infrastructure may not dominate the market, it serves as an essential component in the charging network, providing convenience and supporting the expansion of electric vehicle usage. The availability of charging infrastructure at retail locations can also result in increased foot traffic and potential customer engagement opportunities for retail businesses.
Hospitality
The hospitality sector plays a crucial role in the development of the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market, but it is unlikely to dominate the market. Hotels, resorts, and other hospitality establishments can provide charging infrastructure to cater to the needs of their guests with electric vehicles. However, the dominance of the hospitality part may be limited due to factors such as the availability of charging infrastructure in other parts like fleets and retail, as well as the focus on developing more extensive charging networks at public places and highways.
Roadside Station
While roadside stations are an integral sector of the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market, they are not expected to dominate the market. Roadside stations, also known as public charging stations, are crucial for supporting long-distance travel and addressing range anxiety. However, the dominance may be limited due to the presence of other parts like fleets, retail, and workplace charging. The focus on building a comprehensive charging network, which includes various parts, ensures accessibility and convenience, reducing the reliance on a single part like roadside stations.
Others
The Others category refers to the remaining applications not categorized under residential, workplace, retail, hospitality, fleets, or roadside stations. These could include specialized charging infrastructure for specific industries or unique use cases. While this part may contribute to the overall Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market, it is unlikely to dominate. The dominance of fleets, combined with the importance of other well-defined parts, may limit the market share of the "Others" part. Nevertheless, it remains an important area of consideration for niche charging infrastructure requirements.
Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market Regional Insights:
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific is expected to dominate the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure market. This can be attributed to the rapid growth and adoption of electric vehicles in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. These countries have implemented strong government initiatives and policies to promote electric vehicles, such as providing subsidies and incentives for both vehicle purchases and the development of charging infrastructure. Furthermore, the increasing urbanization, rising disposable income, and growing awareness about environmental sustainability in the region are driving the demand for electric vehicles and charging infrastructure. The presence of major electric vehicle manufacturers and charging infrastructure providers in Asia Pacific also contributes to its dominance in this market.
North America
North America is one of the key regions in the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure market. The region has witnessed significant growth in the adoption of electric vehicles, especially in the United States, Canada, and some parts of Mexico. Factors such as government support in the form of tax incentives and subsidies for electric vehicle purchases, favorable regulations, and increasing investments in charging infrastructure development have contributed to the growth of the market in North America. Additionally, the presence of established electric vehicle manufacturers, such as Tesla, and the growing number of public and private charging stations further support the dominance of North America in this market.
Europe
Europe is another strong contender in the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure market. Several European countries, including Norway, the Netherlands, and Germany, have set ambitious targets for electric vehicle adoption, backed by supportive government policies and regulations. The region has a well-developed network of charging infrastructure, including both public and private charging stations, making it convenient for electric vehicle owners. Additionally, collaborations between automotive manufacturers, energy companies, and infrastructure providers have boosted the growth of the market in Europe. The increasing focus on sustainable transportation and the rising awareness about air pollution and climate change in the region will continue to drive the demand for electric vehicle charging infrastructure.
Latin America
Latin America is gradually gaining traction in the Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure market. While the region is still in the early stages of electric vehicle adoption, countries like Brazil, Mexico, and Chile are showing promising growth in terms of infrastructure development and electric vehicle sales. The increased government efforts, such as tax incentives and investment in charging infrastructure projects, are stimulating the market's growth in Latin America. Moreover, the region's abundant renewable energy resources, notably hydropower, offer potential for sustainable charging infrastructure solutions. However, challenges such as limited charging infrastructure availability and affordability of electric vehicles may hinder the rapid dominance of Latin America in this market.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region is gradually witnessing growth in the Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure market. The United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa are emerging as key markets for electric vehicles and charging infrastructure in the region due to supportive government policies and incentives. The presence of well-established charging network providers and partnerships with international companies contribute to the growth of the market in this region. However, challenges such as limited public charging infrastructure and the need for further investment and infrastructure development may slow down the dominance of the Middle East & Africa in the global market.
Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market Competitive Landscape:
Prominent figures within the worldwide electric vehicle charging infrastructure industry play a vital role in the development, production, and installation of charging stations. Additionally, they offer innovative solutions for electric vehicle charging networks, contributing significantly to the expansion and acceptance of electric vehicles on a global scale.
Prominent companies active in the Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market are Tesla Inc., ChargePoint Inc., Schneider Electric SE, ABB Ltd., Siemens AG, Blink Charging Co., EVBox, Engie SA, Webasto Group, and Efacec Power Solutions. Tesla Inc. is a well-known American company specializing in electric vehicles and sustainable energy solutions. ChargePoint Inc. is recognized for its cutting-edge electric vehicle charging stations. Schneider Electric SE, ABB Ltd., and Siemens AG are renowned global technology firms offering a diverse array of energy management innovations. Blink Charging Co. stands out as a leading provider of EV charging equipment and networked services. EVBox, a Dutch firm, concentrates on developing, installing, and maintaining electric vehicle charging solutions. Engie SA is a prominent French multinational electric utility firm, while the Webasto Group is primarily involved in manufacturing roof and heating systems for various industries, including electric vehicles. Efacec Power Solutions, a Portuguese company, delivers energy, engineering solutions, and charging systems tailored for electric vehicles.
Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market COVID-19 Impact and Market Status:
The global market for electric vehicle charging infrastructure has experienced a notable decline in growth as a result of the Covid-19 pandemic, with disruptions in the supply chain and a decrease in demand playing key roles.
The pandemic caused by COVID-19 has deeply impacted the market for electric vehicle charging infrastructure. Initially, there was a decrease in demand for electric vehicles due to lockdowns and limited movement, resulting in a slowdown of the market as many charging infrastructure projects were postponed or disrupted. Over time, however, the pandemic has underscored the importance of sustainability and emission reduction, leading to a renewed emphasis on electric vehicles and the necessity for reliable charging infrastructure. Governments and industry stakeholders are now actively promoting the adoption of electric vehicles and fast-tracking the expansion of charging networks by offering incentives such as subsidies, grants, and tax breaks to attract investments. As the global economy gradually recovers from the pandemic, the market for electric vehicle charging infrastructure is expected to recover and experience substantial growth. However, this recovery may be influenced by aspects like the availability of charging infrastructure, advancements in battery technology, and the general public's perception and acceptance of electric vehicles.
Recent Trends & Innovations of the Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market:
- In May 2021, Shell New Energies acquired Ubitricity, a leading provider of on-street electric vehicle charging solutions.
- In April 2021, ChargePoint, a major electric vehicle infrastructure company, announced a merger with Switchback Energy Acquisition Corporation, with plans to go public by the end of the year.
- In March 2021, EVBox Group acquired Everon, a Dutch charging management and solutions provider, strengthening its position in the European electric vehicle charging market.
- In January 2021, ChargePoint raised $127 million in a new funding round, allowing the company to expand its electric vehicle charging network.
- In December 2020, EVgo, an American electric vehicle charging network operator, announced its plans to go public through a merger with Climate Change Crisis Real Impact I Acquisition Corporation (CLII).
- In November 2020, Volkswagen announced its investment of €450 million in EnBW, a German utility company, to develop and expand a high-power electric vehicle charging network across Europe.
- In October 2020, Tesla unveiled its new "teardrop" Supercharger design, with a more compact footprint and additional flexibility for installations in urban areas.
- In September 2020, EVgo partnered with General Motors to add more than 2,700 fast-charging stations across the US, aiming to make electric vehicle charging more convenient and accessible.
- In August 2020, Electrify America announced its collaboration with Love's Travel Stops, a national travel stop network, to install ultra-fast electric vehicle charging stations at select locations along highways.
- In June 2020, BP Ventures made an equity investment of €1 million in Powershare, a China-based provider of integrated hardware and software electric vehicle charging solutions.
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market Growth Factors:
The development catalysts for the Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market encompass escalating governmental backing and financial investment, surging environmental awareness, and broadening uptake of electric vehicles.
The market for Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure is witnessing significant expansion for several reasons. The escalating global embrace of electric vehicles (EVs) is a primary driver for the increasing demand for charging infrastructure. With a rising number of consumers and businesses transitioning to EVs, the necessity for efficient and easily accessible charging stations is becoming increasingly crucial. Concurrently, governmental efforts and incentives aimed at curbing greenhouse gas emissions and addressing climate change are also catalyzing the market's growth trajectory. Numerous countries are instituting policies that promote the development of charging infrastructure by offering subsidies for installation costs and tax benefits to EV charging station proprietors. Furthermore, technological progressions are facilitating quicker charging intervals and enhanced charging capacity, rendering EVs more convenient and attractive to consumers. Substantial investments by key market stakeholders such as automakers, energy firms, and manufacturers of EV charging stations are driving market expansion. These investments are geared towards bolstering the charging infrastructure network, broadening geographical coverage, and enhancing user experience. Additionally, the transition towards renewable energy sources is spurring the installation of EV charging stations powered by sustainable energy, fostering a more environmentally friendly transportation system. In essence, the notable growth catalysts of the Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market encompass ened EV adoption rates, government backing, technological innovations, and substantial industry investments.
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market Restraining Factors:
The growth of the Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market is impeded by the scarcity of charging stations and the substantial infrastructure expenses that are involved.
The market for electric vehicle charging infrastructure has experienced substantial growth in recent times, propelled by the rising popularity of electric vehicles worldwide. However, the market's expansion is being hindered by various obstacles. One significant challenge is the substantial initial investment required for installing charging stations, which is discouraging potential investors and limiting the growth of the charging infrastructure network. Another obstacle is the limited driving range of electric vehicles and the time-consuming nature of charging, causing range anxiety among consumers and affecting their willingness to switch to electric vehicles. The absence of standardized charging protocols and a universal charging connector presents further challenges by impeding interoperability and convenience, thereby impeding market growth. Moreover, the insufficient number of public charging stations, particularly in rural areas, is a major barrier to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Additionally, the reliance on existing electricity grids and the necessity for grid enhancements to support high-power fast charging stations are hindering the deployment of charging infrastructure. Nevertheless, the electric vehicle charging infrastructure market presents significant prospects, with governments and private entities increasing investments in expanding the charging network, advancements in technology enhancing charging speeds, and efforts underway to standardize charging protocols. These initiatives are anticipated to overcome current barriers and have a positive impact on the future growth of the electric vehicle charging infrastructure market.
Key Segments of the Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market
Offering Overview
• EV Charging Solutions
• EV Charging Services
Portability Overview
• Stationary EV Chargers
• Portable/Mobile EV Chargers
Charging Point Overview
• AC Charger
• DC Charger
Mounting Type Overview
• Wall Mounted Charger
• Pedestal Mounted Charger
Standard Overview
• Megawatt Charging System (MCS)
• Combined Charging System (CCS)
• Others
Phase Overview
• Single Phase
• Three Phase
Charging Level Overview
• Level 1
• Level 2
• Level 3
Application Overview
• Residential
• Workplace
• Retail
• Hospitality
• Fleets
• Roadside Station
• Others
Regional Overview
North America
• US
• Canada
• Mexico
Europe
• Germany
• France
• UK
• Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
• China
• Japan
• India
• Rest of Asia Pacific
Middle East and Africa
• Saudi Arabia
• UAE
• Rest of Middle East and Africa
Latin America
• Brazil
• Argentina
• Rest of Latin America

