Market Analysis and Insights:
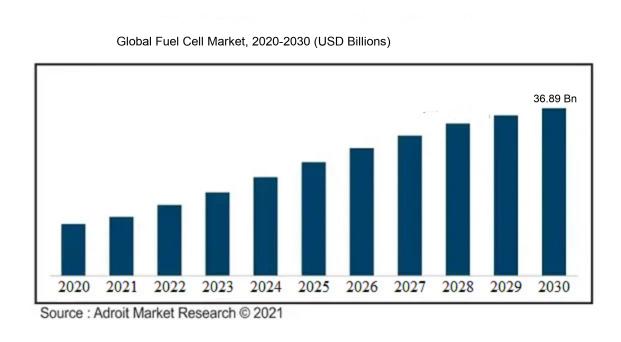
The market for fuel cells was estimated to be worth USD 7.31 billion in 2023, and from 2024 to 2030, it is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 27.21%, with an expected value of USD 36.89 billion in 2030.
The market for fuel cells is experiencing a significant upsurge due to a multitude of factors that are propelling its progress and advancement. A primary catalyst driving this growth is the escalating need for clean and sustainable energy sources. Fuel cells represent an effective and environmentally conscious alternative to traditional power generation methods reliant on fossil fuels. These cells generate electricity through electrochemical reactions, with the only by-products being water vapor and heat. Another key driver is the imperative for a dependable and uninterrupted power source. Fuel cells serve as reliable backup power systems crucial for essential operations such as those in hospitals, data centers, and telecommunications networks, guaranteeing continual functionality during power disruptions. Moreover, enhancements in fuel cell technology, such as ened efficiency, durability, and cost efficiency, have substantially bolstered market expansion.
Furthermore, governmental initiatives and regulations that actively advocate for the adoption of fuel cells, coupled with favorable policies and incentives, have played a significant role in augmenting market demand. The integration of fuel cells across a spectrum of sectors spanning transportation, residential, and industrial domains is contributing to market growth by offering versatile and efficient power solutions. In essence, the fuel cell market is shaped by surging environmental apprehensions, the need for reliable power sources, technological progressions, and supportive governmental regulations, all of which collectively are spearheading its rapid evolution in the foreseeable future.
Fuel Cell Market Scope:
| Metrics | Details |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Historic Data | 2018-2022 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2030 |
| Study Period | 2018-2030 |
| Forecast Unit | Value (USD) |
| Revenue forecast in 2030 | USD 36.89 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 27.21% during 2024-2030 |
| Segment Covered | By Type, By Components, By Fuel, By Size, By Application, By End-use, By Region. |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America, Middle East and Africa |
| Key Players Profiled | Ballard Power Systems, Bloom Energy, FuelCell Energy, Plug Power, AFC Energy, Ceres Power Holdings, Doosan Fuel Cell America, Hydrogenics Corporation, Pearl Hydrogen Technology, and SFC Energy AG. |
Market Definition
A fuel cell is a device that produces electricity by facilitating a chemical reaction between a fuel, hydrogen for example, and an oxidizing agent, usually oxygen extracted from the surrounding air. This electrochemical procedure generates electricity without combustion or the release of harmful emissions, providing a greener and highly effective option compared to conventional energy resources.
Fuel cells are a vital technology due to their ability to produce electricity in a clean and efficient manner. In contrast to conventional internal combustion engines, fuel cells operate by generating electricity through an electrochemical process, resulting in reduced emissions of greenhouse gases and pollutants. Their exceptional energy conversion efficiency makes them well-suited for powering diverse applications such as vehicles, residences, and large-scale energy storage systems. Additionally, fuel cells have the versatility to utilize various fuels, including hydrogen, natural gas, and renewable sources, offering a versatile and eco-friendly solution for power generation. Given the global emphasis on clean energy and climate change mitigation, the widespread adoption of fuel cells is essential in curbing carbon emissions and establishing a more sustainable future.
Key Market Segmentation:

Insights On Key Type
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC)
PEMFC is expected to dominate the Global Fuel Cell Market. The PEMFC technology offers several advantages such as high power density, quick start-up, and flexible fuel options. It is widely used in transportation applications, including passenger vehicles, buses, and forklifts. Additionally, the increasing focus on green energy and stringent emission regulations are driving the demand for PEMFCs. With ongoing research and development in the field, PEMFCs are continuously improving in terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness, further solidifying their position as the dominant part in the global fuel cell market.
Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC)
SOFC is another prominent sector within the Global Fuel Cell Market. SOFCs offer high electrical efficiency and can operate with a variety of fuels, including hydrogen, natural gas, and biogas. They are widely used in stationary power generation applications, such as residential and commercial buildings, as well as in some transportation applications like auxiliary power units for trucks. Although SOFCs have certain limitations such as high operating temperatures and slower start-up times, ongoing research and technological advancements are addressing these challenges and expanding the market potential for SOFCs.
Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell (PAFC)
PAFCs have been widely adopted for stationary power generation applications, particularly in combined heat and power (CHP) systems. They are known for their high tolerance to impurities in fuels and have demonstrated good performance in cogeneration applications, where both electricity and heat are generated. However, PAFCs have lower electrical efficiency compared to other fuel cell types, such as PEMFCs and SOFCs. As a result, their dominance in the global fuel cell market is limited to specific applications where their unique features are advantageous.
Alkaline Fuel Cell (AFC)
AFCs have a long history and were one of the first types of fuel cells to be developed. They have been primarily used in aerospace applications, but their market presence has significantly diminished over time due to several limitations. AFCs require high-purity hydrogen fuel and have relatively low power density compared to other fuel cell types. Moreover, their sensitivity to carbon dioxide and other impurities in fuel restricts their widespread adoption. Therefore, AFCs are not expected to dominate the global fuel cell market.
Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC)
MFCs are a niche sector within the Global Fuel Cell Market. They utilize bacteria or other microorganisms to generate electricity from organic matter. MFCs have potential applications in waste treatment, particularly in harnessing energy from wastewater. However, their commercialization and scalability remain as challenges. The low power output, slow reaction rates, and limited understanding of the microbial processes involved restrict the dominant presence of MFCs in the global fuel cell market.
Others
The Others category includes various types of emerging fuel cell technologies that are still in the early stages of development or have limited commercial reach. This may include direct methanol fuel cells, molten carbonate fuel cells, and more. While these technologies may possess certain unique features, they are yet to establish dominance in the global fuel cell market. Ongoing research and development efforts will determine their future potential and competitiveness in the market.
Insights On Key Components
Stack
The stack is expected to dominate the Global Fuel Cell Market. This component is crucial as it is the heart of a fuel cell system, where the electrochemical processes take place. The stack consists of multiple layers of electrodes and electrolytes that facilitate the conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy. Given its central role in the fuel cell system and its direct impact on the efficiency and performance of the technology, the stack is likely to dominate the market.
Balance of Plant
The balance of plant, while essential to the functioning of a fuel cell system, is expected to play a supporting role rather than dominate the Global Fuel Cell Market. This part includes components such as thermal management systems, humidifiers, power conditioning units, and control systems. While these components are vital for the overall operation and optimization of fuel cell systems, they do not have the same direct influence on the system's efficacy as the stack. Therefore, although the balance of plant is necessary, it is less likely to be the dominant part.
Insights On Key Fuel
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is expected to dominate the global fuel cell market. As the most widely used fuel source for fuel cells, hydrogen offers several advantages including high energy density, zero emissions, and fast refueling times. Additionally, hydrogen fuel cells have already been widely adopted in various sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and stationary power generation. Governments and industries around the world are investing heavily in hydrogen infrastructure and research, further promoting the use of hydrogen fuel cells. With ongoing advancements in hydrogen production, storage, and distribution, hydrogen is poised to maintain its dominance in the global fuel cell market.
Ammonia
Ammonia, although being a potential alternative fuel for fuel cells, is not expected to dominate the global fuel cell market. While ammonia has advantages such as high energy density and ease of storage, it still faces challenges in terms of infrastructure and fuel cell technology compatibility. Ammonia fuel cells require specific catalysts and materials, which are not as well-developed as those for hydrogen fuel cells. Additionally, the production and distribution of ammonia involve more complex processes compared to hydrogen. Although ammonia may find niche applications in specific industries, such as transportation and heavy machinery, it is unlikely to surpass hydrogen as the dominant fuel cell part.
Methanol
Methanol is another fuel that is not expected to dominate the global fuel cell market. While methanol fuel cells have been extensively studied and utilized in portable and backup power applications, they face challenges related to safety, toxicity, and infrastructure. Methanol also requires reforming processes to extract hydrogen before being used in fuel cells, adding complexity and cost. Moreover, the lower energy density of methanol compared to hydrogen limits its suitability for applications that require longer operating times or higher power outputs. As a result, while methanol may continue to play a role in some specific applications, it is unlikely to become the dominant part in the fuel cell market.
Ethanol
Ethanol as a fuel is not expected to dominate the global fuel cell market. Similar to methanol, ethanol fuel cells have primarily found applications in portable and small-scale power systems. However, ethanol fuel cells face challenges related to lower energy density compared to hydrogen, as well as issues of fuel purity and limited infrastructure. Ethanol also requires reforming processes for hydrogen extraction, which can add complexity and cost to the fuel cell system. Although there may be niche applications for ethanol fuel cells, such as in the automotive industry, the dominance of hydrogen fuel cells and the challenges associated with ethanol limitations make it unlikely to become the leading part in the global fuel cell market.
Hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbon fuel cells, including fossil fuels like natural gas and gasoline, are not expected to dominate the global fuel cell market. While hydrocarbon fuel cells offer advantages such as high energy density and existing infrastructure, they face significant challenges in terms of emissions, environmental concerns, and long-term sustainability. Hydrogen fuel cells, on the other hand, provide a cleaner energy alternative with zero emissions and are more aligned with global efforts to mitigate climate change. As a result, the dominance of hydrogen and the environmental consciousness surrounding fuel cell technology make hydrocarbon fuel cells unlikely to become the leading part in the global fuel cell market.
Insights On Key Size
Large Scale
The Large Scale size is expected to dominate the Global Fuel Cell Market. This is because large-scale fuel cell systems are primarily used for industrial applications, such as power generation for large facilities or utility-scale electricity production. These systems have a high power output and are designed to meet the energy demands of large-scale operations. Additionally, advancements in technology, such as improved efficiency and cost reduction, have made large-scale fuel cell systems more attractive for industries looking to transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. Therefore, the Large Scale part is expected to have a significant presence in the Global Fuel Cell Market.
Small Scale
The Small Scale size, while not expected to dominate the Global Fuel Cell Market, still holds considerable potential. Small-scale fuel cells are commonly used in residential, commercial, and portable applications. These include home backup power systems, mobile devices, portable power generators, and even small vehicles. The demand for decentralized power generation and the shift towards greener energy sources present opportunities for the Small Scale part. However, various challenges, such as higher costs and limited power output, may limit its dominance. Nevertheless, the increasing adoption of fuel cell technology in various small-scale applications indicates its potential for growth and market presence.
Insights On Key Application
Fuel Cell Vehicles
The Fuel Cell Vehicles is expected to dominate the Global Fuel Cell Market. This is primarily due to the increasing focus on reducing carbon emissions and the growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions. Governments around the world are implementing stricter regulations on vehicle emissions, which is driving the adoption of fuel cell vehicles. Additionally, advancements in fuel cell technology and the establishment of hydrogen refueling infrastructure are further supporting the growth of this part. Fuel cell vehicles offer several advantages such as longer driving ranges, shorter refueling times, and zero tailpipe emissions, making them a compelling alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
Portable
The Portable sector of the Application category is also expected to contribute significantly to the Global Fuel Cell Market. Portable fuel cells are compact, lightweight, and provide a portable power source for various applications such as consumer electronics, military devices, and remote power generation. The increasing demand for portable electronic devices, including smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices, is driving the growth of this part. Moreover, the need for clean and reliable power sources in off-grid and emergency situations is further fueling the demand for portable fuel cells.
Stationary
The Stationary sector of the Application category is another important component in the Global Fuel Cell Market. Stationary fuel cells are widely used for power generation in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. They offer high energy efficiency, low emissions, and can operate continuously for extended periods. The growing focus on decentralized power generation, coupled with the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, is driving the demand for stationary fuel cells. Additionally, favorable government policies and incentives promoting clean energy solutions are expected to further boost the deployment of stationary fuel cells in various applications.
Others
The remaining sectors in the Application category, labeled as Others, includes various niche applications of fuel cells such as material handling equipment, backup power systems, and portable generators. While these applications have their own significance and niche markets, they are expected to have a relatively smaller share in the overall Global Fuel Cell Market. Nonetheless, the demand for fuel cells in these applications is driven by factors such as energy efficiency, reduced emissions, and increased reliability. Continued advancements in fuel cell technology and cost reductions may further enhance the adoption of fuel cells in these niche applications.
Insights On Key End-use
Residential
The Residential end-use is expected to dominate the Global Fuel Cell market. This is primarily due to the increasing demand for clean and reliable power generation solutions in residential settings. Fuel cells provide an efficient and sustainable alternative to traditional energy sources, offering benefits such as reduced emissions and improved energy independence. As individuals and households become more conscious of their environmental impact, the adoption of fuel cell technologies in residential applications, such as distributed power generation and heating, is on the rise. Moreover, government initiatives promoting the use of fuel cells in residential sectors further contribute to the dominance of this part. With advancements in technology and growing awareness, the Residential part is projected to experience significant growth in the coming years.
Commercial & Industrial
The Commercial & Industrial end-use of the Global Fuel Cell market holds great potential for growth and innovation. The commercial sector encompasses a wide range of applications, including office buildings, retail spaces, hotels, and hospitals, where fuel cells can provide a reliable and uninterrupted power supply. The industrial sector, on the other hand, comprises applications in manufacturing, energy-intensive processes, and large-scale facilities. Fuel cells offer advantages such as increased energy efficiency, reduced emissions, and operational cost savings, making them an attractive solution for commercial and industrial users. Despite this potential, the Commercial & Industrial part is not expected to dominate the market due to the higher dominance and growth potential of other parts.
Transportation
The Transportation end-use of the Global Fuel Cell market is poised for growth, driven by the increasing adoption of fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). FCVs offer a cleaner alternative to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles, as they produce zero emissions during operation. With strict emission regulations and the need for sustainable transportation solutions, several governments and automotive manufacturers are investing in the development of FCVs and the necessary infrastructure. While the Transportation part shows promise, it is not projected to dominate the market due to factors such as limited infrastructure, high initial costs, and the dominance of other parts.
Data Centers
Data Centers represent another end-user of the Global Fuel Cell market that holds potential for growth. Fuel cells offer a reliable and efficient power backup solution for data centers, ensuring uninterrupted operations in the event of grid outages. By providing backup power, fuel cells can help data centers mitigate the risks associated with power disruptions, data loss, and downtime. Additionally, fuel cells produce low or zero emissions, aligning with the sustainability goals of data center operators. Despite these advantages, the Data Centers part is not expected to dominate the market, given the dominance and growth potential of other parts.
Military & Defense
The Military & Defense end-use of the Global Fuel Cell market is characterized by its unique set of requirements and applications. Fuel cells offer distinct advantages to the military and defense sector, including quiet operation, reduced logistics burden, and extended mission capabilities. These attributes make fuel cells suitable for various applications, such as portable power systems, unmanned vehicles, and soldier-worn devices. However, due to the comparatively niche nature of this part and the lower market size, it is not expected to dominate the overall market.
Utilities & Government/Municipal Institutes
The Utilities & Government/Municipal Institutes end-use of the Global Fuel Cell market represents the adoption of fuel cells in utility-scale power generation and public infrastructure. Fuel cells can provide grid-independent power solutions, especially in remote and off-grid locations where extending the electrical grid might be costly or impractical. Additionally, fuel cells have the potential to support decentralized energy systems and foster energy resiliency in the face of natural disasters or grid failures. Although the Utilities & Government/Municipal Institutes part offers interesting prospects, it is not projected to dominate the market due to the dominance and growth potential of other parts.
Insights on Regional Analysis:
North America
North America is expected to dominate the global fuel cell market. The region is witnessing significant growth in the adoption of fuel cell technologies, driven by the increasing focus on renewable energy and the transition towards cleaner and more sustainable power sources. The United States, in particular, holds a prominent position in the market due to the strong presence of key market players, supportive government initiatives, and the high demand for fuel cell vehicles. Additionally, the region has a well-established hydrogen infrastructure and a robust research and development ecosystem, further fueling the growth of the fuel cell market in North America.
Latin America
Latin America is steadily emerging as a key player in the global fuel cell market. The region is witnessing a growing interest in fuel cell technologies, primarily driven by the increasing need to diversify the energy mix and reduce reliance on conventional fossil fuels. Countries like Brazil and Mexico are taking initiatives to promote the use of fuel cells, particularly in the transportation sector. Additionally, the abundant availability of renewable energy resources, such as solar and wind power, in several Latin American countries presents a significant opportunity for the growth of fuel cell technologies in the region. However, limited infrastructure and awareness about fuel cell technology remain key challenges for market development in Latin America.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific is poised to witness substantial growth in the global fuel cell market. The region is home to major economies like China, Japan, and South Korea, which have been at the forefront of adopting fuel cell technologies. These countries have implemented supportive policies and incentives to promote fuel cell vehicles and the deployment of stationary fuel cells in various applications. The increasing focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving air quality, and developing sustainable energy systems is expected to drive the demand for fuel cells in the Asia Pacific region. Furthermore, the presence of well-established manufacturing capabilities, research and development facilities, and a growing hydrogen infrastructure contribute to the dominance of Asia Pacific in the global fuel cell market.
Europe
Europe represents a significant market for fuel cell technologies. The region has been actively pursuing the decarbonization of the energy sector and has set ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Several European countries, including Germany, the UK, and Norway, have implemented favorable policies and financial incentives to encourage the adoption of fuel cells. Additionally, the region has a well-developed hydrogen infrastructure and strong research and development capabilities. Europe's commitment to clean energy and the growing demand for fuel cell vehicles are key factors contributing to the dominance of the region in the global fuel cell market.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region is expected to play a relatively smaller role in the global fuel cell market compared to other regions. The limited adoption of fuel cell technologies in the region can be attributed to various factors, including the abundance of conventional fossil fuels, the availability of relatively cheaper energy options, and the nascent stage of development in the clean energy sector. Nonetheless, some countries in the region, particularly the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia, have started exploring fuel cell applications for niche industries and off-grid power generation. Although the region may not dominate the global fuel cell market, there is potential for future growth as the focus on sustainable energy intensifies in the Middle East & Africa.
Overall, while North America is expected to dominate the global fuel cell market, the other regions also exhibit significant potential for growth and adoption of fuel cell technologies. Each region presents unique opportunities and challenges, driven by factors such as government policies, infrastructure development, and the demand for clean energy alternatives.
Company Profiles:
Ballard Power Systems is a prominent figure in the international fuel cell sector, with a focus on advancing clean energy technologies through the creation and implementation of innovative fuel cell solutions.
Prominent companies in the fuel cell industry comprise Ballard Power Systems, Bloom Energy, FuelCell Energy, Plug Power, AFC Energy, Ceres Power Holdings, Doosan Fuel Cell America, Hydrogenics Corporation, Pearl Hydrogen Technology, and SFC Energy AG. Each entity specializes in distinct areas within the fuel cell sector. Ballard Power Systems is recognized for its proton exchange membrane fuel cell innovations. Bloom Energy excels in the field of solid oxide fuel cell technology. FuelCell Energy is known for its expertise in delivering fuel cell power plant solutions. Plug Power focuses on developing hydrogen fuel cell systems for a variety of applications, including material handling and stationary purposes. AFC Energy is a key player in the advancement and commercialization of alkaline fuel cells. Ceres Power Holdings stands out for its pioneering work in solid oxide fuel cell technology. Doosan Fuel Cell America is dedicated to providing clean energy solutions through its fuel cell technology. Hydrogenics Corporation is a global frontrunner in offering solutions for hydrogen generation, energy storage, and fuel cell power applications. Pearl Hydrogen Technology is actively involved in the development of fuel cell systems and hydrogen gas solutions. Lastly, SFC Energy AG is recognized for its hybrid power solutions centered around fuel cell technology. These companies collectively drive the expansion and progress of the fuel cell market through their innovative contributions and advancements.
COVID-19 Impact and Market Status:
The Global Fuel Cell market has experienced disruptions in supply chains and decreased demand from critical sectors like automotive and aerospace due to the effects of the Covid-19 pandemic.
The global fuel cell market has faced significant repercussions due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lockdown measures and travel restrictions imposed by countries worldwide have resulted in a notable decrease in the demand for fuel cells across various sectors such as automotive, power generation, and portable devices. The stringent lockdowns and reduced economic activities have led to supply chain disruptions, causing delays in the production and distribution of fuel cell systems and components. Furthermore, the pandemic-induced uncertainty and economic downturn have negatively impacted investor confidence, leading to decreased investments and funding for fuel cell research and development initiatives. Despite these challenges, the crisis has underscored the importance of clean and sustainable energy solutions, potentially stimulating future demand for fuel cells. As countries shift their focus towards economic recovery and green stimulus packages, there may arise opportunities for the fuel cell market to recover. Nevertheless, the immediate effects of the pandemic have translated into a decrease in demand and supply chain interruptions for fuel cell technologies.
Latest Trends and Innovation:
- In April 2020, Ballard Power Systems announced the signing of a Technology Solutions agreement with Audi AG, aiming to accelerate the development of hydrogen fuel cell technology for transportation applications.
- In January 2021, Plug Power Inc. completed its acquisition of United Hydrogen Group Inc., a leading supplier of green hydrogen sourced from renewable energy.
- In November 2019, FuelCell Energy Inc. announced a strategic collaboration with Drax Power Station in the UK to explore the potential of using fuel cells to capture carbon dioxide emissions.
- In December 2020, Bloom Energy and Samsung Heavy Industries announced a collaboration to develop and market solid oxide fuel cells for marine applications, enabling the utilization of cleaner energy sources in the shipping industry.
- In May 2021, Cummins Inc. launched its new PEM electrolyzer to produce hydrogen as a clean fuel, enabling the company to expand its offerings in the hydrogen fuel cell market.
- In September 2020, Doosan Fuel Cell entered into a collaboration with Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering to develop solid oxide fuel cell technology for maritime applications, aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the shipping industry.
- In March 2021, Ballard Power Systems signed a Memorandum of Understanding with Linamar Corporation to jointly develop and commercialize fuel cell powertrains for light-duty vehicles.
- In October 2020, Toyota and Hino Motors announced a joint venture called Hino Motors Fuel Cell to develop and manufacture fuel cell systems for commercial trucks, accelerating the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell technology in the transportation sector.
- In January 2021, Hydrogenics Corporation, a subsidiary of Cummins Inc., announced a partnership with The Linde Group to deliver hydrogen fuel cell systems for stationary power applications, expanding their presence in the industrial and energy sectors.
- In June 2021, Plug Power Inc. and SK Group announced a strategic partnership to accelerate the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell technology in South Korea, focusing on various applications such as mobility, energy, and infrastructure.
Significant Growth Factors:
Factors propelling the expansion of the fuel cell industry comprise escalating governmental backing for sustainable energy, surging interest in electric vehicles, and progressions in fuel cell technology.
The fuel cell industry has experienced significant growth in recent years due to various factors. One key driver has been the rising global demand for cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, leading to a surge in the utilization of fuel cells as a reliable and environmentally friendly power generation alternative. The increasing emphasis on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and addressing climate change has also been a significant factor fuelling the expansion of the market. Fuel cells are preferred over traditional power generation methods due to their lower carbon footprint, making them an attractive option across different industries. Moreover, ongoing advancements in fuel cell technology have enhanced their efficiency and durability, making them increasingly feasible for commercial applications. This has resulted in their widespread adoption in sectors such as automotive, residential, and portable power devices. Government support in the form of funding and favorable policies has played a crucial role in stimulating the growth of the fuel cell market by promoting the adoption of cleaner energy sources and encouraging innovation within the industry. Additionally, continued investments in research and development efforts to enhance fuel cell performance and reduce costs are further propelling market expansion. Overall, the future outlook for the fuel cell market remains optimistic, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions and ongoing technological progress within the sector.
Restraining Factors:
Challenges facing the fuel cell market include the restricted availability of hydrogen infrastructure and the elevated production expenses.
The fuel cell industry has been gaining momentum in recent years, holding the potential to transform the energy generation and consumption landscape.
However, there exist various obstacles that hinder the expansion and widespread acceptance of fuel cell technology. A fundamental challenge lies in the high cost associated with fuel cell systems, acting as a significant deterrent for both consumers and businesses.
Key Segments of the Fuel Cell Market
Type Overview
• Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
• Solid Oxide Fuel Cell
• Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell
• Alkaline Fuel Cell
• Microbial Fuel Cell
• Others
Components Overview
• Stack
• Balance of plant
Fuel Overview
• Hydrogen
• Ammonia
• Methanol
• Ethanol
• Hydrocarbon
Size Overview
• Small Scale
• Large Scale
Application Overview
• Portable
• Stationary
• Fuel Cell Vehicles
• Others
End-Use Overview
• Residential
• Commercial & Industrial
• Transportation
• Data Centers
• Military & Defense
• Utilities & Government/Municipal Institutes
Regional Overview
North America
• US
• Canada
• Mexico
Europe
• Germany
• France
• U.K
• Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
• China
• Japan
• India
• Rest of Asia Pacific
Middle East and Africa
• Saudi Arabia
• UAE
• Rest of Middle East and Africa
Latin America
• Brazil
• Argentina
• Rest of Latin America

