Market Analysis and Insights
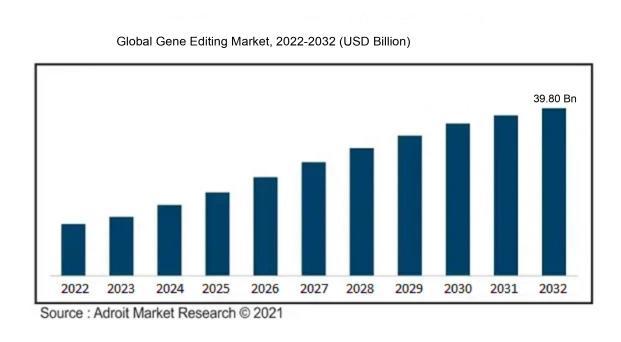
The market for gene editing was estimated at USD 6.03 billion in 2022 and is anticipated to increase from USD 7.20 billion in 2023 to USD 39.80 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.11% over the forecast period (2023 - 2032).
With the use of gene editing, it may be possible to improve the features of crops and livestock, such as disease resistance, greater nutritional value, and increased production, so promoting food security.
Gene Editing Market Scope:
| Metrics | Details |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Historic Data | 2018-2022 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Study Period | 2018-2032 |
| Forecast Unit | Value (USD) |
| Revenue forecast in 2032 | USD 39.80 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 20.11% during 2022-2032 |
| Segment Covered | by Application , Technology , End User,by Region. |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America Middle East and Africa |
| Key Players Profiled | Lonza Group Ltd., Merck KGaA, Sangamo Therapeutics, Inc., CRISPR Therapeutics AG, Intellia Therapeutics, Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Horizon Discovery Group plc, New England Biolabs, Inc., GenScript Biotech Corporation, Editas Medicine, Inc., and Precision Biosciences, Inc. |
Market Definition
Gene editing is the act of altering an organism's DNA, frequently with the use of specialized instruments and methods.
It enables adding, deleting, or modifying certain genetic material from an organism's genome. Through direct genetic code manipulation, gene editing has the power to change an organism's features, behaviors, and even functions.
One of the most widely used and well-known gene editing techniques is the CRISPR-Cas9 system. A section of DNA known as CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) comprises repeating sequences, and Cas9 is a protein that functions as molecular scissors. Together, they may be trained to precisely cut DNA at a predetermined point inside the genome. Once the DNA is cut, the cell's built-in repair processes can be used to add modifications to the genetic code.
By altering or turning off certain genes in model organisms, gene editing enables researchers to investigate the biological roles of individual genes. Gene editing can be utilized to create possible genetic condition therapies. It shows promise for treating disorders with a genetic foundation by replacing or repairing defective genes responsible for diseases. Crops with better features, such as disease resistance, greater yield, and improved nutritional value, can be developed through gene editing. In order to produce animals with desirable qualities, such as improved meat quality or disease resistance, gene editing can be used. This might be advantageous for agriculture and food service .
Key Market Segmentation

Insights on Technology
The CRISPR Segment Valued for the Highest Share
The Genome Editing Market was controlled by the CRISPR sector technologically. The main reason for this is its expanded use in biotechnology, agriculture, and healthcare. Huntington's disease (HIV) and the human immunodeficiency virus (CRISPR/Cas9) are two significant diseases for which research is being conducted.
Insights on Application
The Cell Line Engineering Segment Valued for the Highest Share
According to the application, cell line engineering held the largest market share. It is largely because of its wide-ranging use in biology, pharmacy, agriculture, and other disciplines. Cell line engineering is the process of assembling collections of cells from a single tissue type (such as an organ or a plant's xylem) in order to preserve uniformity in the tissue that results. Cell lines are frequently used in the creation of vaccines, protein synthesis, artificial tissue, and drugs. Because of the depth of the field's study, more than 36,000 cell lines have been created for use in pharmacogenomics, healthcare, and academia.
Insights on Region
The North American Region Accounted for the Highest Share
North America is predicted to have a sizable market share for genome editing globally throughout the forecast period. The region's market is expected to expand in the coming years as a result of the development of gene therapy in the United States, an increase in the consumption of genetically modified crops, an increase in the prevalence of infectious diseases and cancer, and the accessibility of research grants and funding.
Key Company Profiles
The key players operating in the gene editing market include Lonza Group Ltd., Merck KGaA, Sangamo Therapeutics, Inc., CRISPR Therapeutics AG, Intellia Therapeutics, Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Horizon Discovery Group plc, New England Biolabs, Inc., GenScript Biotech Corporation, Editas Medicine, Inc., and Precision Biosciences, Inc.
COVID-19 Impact and Market Status
Due to lockdowns and safety precautions, several research institutions and laboratories were temporarily closed or functioned at reduced capacity. Projects that were already underway, especially those involving gene editing, were hampered by this disturbance.
The financing for gene editing research and development initiatives may have been impacted by changes in funding priorities and economic uncertainty. It's possible that some investors have switched their funding to pandemic-related initiatives. Disruptions in the global supply chain could have slowed down research by limiting the availability of the tools, reagents, and other necessary components required for gene editing operations. The pandemic may have slowed down or altered clinical studies for gene editing medicines or treatments, delaying the release of new therapeutics.
Changes in objectives and resources within regulatory agencies may have had an impact on the regulatory procedures and approvals for gene editing medicines and goods. Research teams working on gene-editing projects that demand close collaboration and hands-on experimentation may have faced difficulties as a result of the transition to remote work and virtual collaboration.
Latest Trends
1. Even as the CRISPR-Cas9 technology revolutionized gene editing, scientists were working hard to increase its accuracy, effectiveness, and specificity. To enable more precise and controlled alterations of DNA, new and updated CRISPR technologies, including base editing and prime editing, were being created.
2. The discovery of gene treatments has led to a huge increase in the gene editing business. In order to cure a range of genetic problems, including uncommon diseases and ailments with a recognized genetic basis, such as sickle cell anemia and specific forms of blindness, researchers were investigating gene editing techniques. Beyond conventional gene therapy, gene editing was being used.
3. Research was concentrated on novel methods for delivering gene editing tools to target cells. It was being investigated how to make viral vectors, nanoparticles, and other delivery systems better in order to increase the effectiveness and security of gene editing.
4. In order to lessen the unintentional DNA alterations caused by off-target consequences of gene editing tools, researchers were developing ways. This was essential for guaranteeing the accuracy and safety of gene-editing medicines.
5. Discussions over the regulatory, legal, and ethical frameworks for gene editing were becoming more and more intense. It was becoming more crucial to provide acceptable rules for the use of gene editing in many applications.
Significant Growth Factors
One of the main factors influencing market expansion was the promise of gene editing for treating hereditary diseases such as sickle cell disease, muscular dystrophy, and specific forms of cancer. Particularly noteworthy developments were made in CRISPR-based treatments.
Genetic research has become more effective and accessible because of techniques like CRISPR-Cas9, which enable the study of gene function, disease processes, and possible treatment targets.
Gene editing was being used to create microbes that might produce biofuels, paper chemicals, and medicines, with potential advantages for sustainable production and industrial operations.
Investment in gene editing research and development was being driven by a growing interest from both the public and private sectors, including venture capital firms and pharmaceutical corporations.
The potential for precise and effective DNA alterations was growing as a result of ongoing improvements in gene editing methodologies and delivery systems.
Restraining Factors
The possibility of unintentional DNA modifications (off-target effects), which might have unanticipated implications and safety issues, was one of the key problems with gene editing.
The moral ramifications of tampering with the human germline or dispersing genetically modified organisms in the environment presented severe ethical and legal issues that required careful examination.
It is still technically difficult to effectively distribute gene editing tools to target cells and tissues, particularly in vivo (inside the body).
It was necessary to do a detailed examination of the long-term impact of gene editing on an organism's health and the possibility of unforeseen repercussions. The speed of research and cooperation may be impacted by legal disputes over intellectual property rights and patents for gene editing.
Recent Developments in the Global Gene Editing Market: A Snapshot
• On January 20, 2022, CRISPR Therapeutics AG and Capsida Biotherapeutics Inc. signed a strategic partnership to develop novel gene therapies using the CRISPR/Cas9 technology for the treatment of various ailments. The agreement states that Capsida will offer its AAV (adeno-associated virus) delivery technology and that CRISPR Therapeutics would donate its genome editing knowledge.
• In July 2021, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. launched its brand-new Invitrogen GeneArt CRISPR Nuclease mRNA and AAV service, allowing researchers to select the ideal delivery method for their genome editing projects. Thermo Fisher's expertise in gene editing delivery is combined with high-quality CRISPR nucleases in the new service to expedite research endeavors.
Key Segments of Gene Editing Market
by Application
1. Cell Line Engineering
2. Genetic Engineering
3. Drug Discovery
4. Gene-modified Cell Therapy
5. Diagnostics
Applications Overview
• Technology
• CRISPR
• TALEN
• ZFN
• Other Technologies
End User Overview
• Academics & Government Institutes
• Biotechnology & Pharma Companies
• Contract Research Organizations
Regional Overview
North America
• U.S
• Canada
Europe
• Germany
• France
• UK
• Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
• China
• India
• Japan
• Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
• Mexico
• Brazil
• Rest of South America

