Market Analysis and Insights
By 2032, the global in-memory computing market is anticipated to have grown to a value of US$ 77.09 billion, up from US$ 15.08 billion in 2022, with a CAGR of 7.12% from 2022 to 2032.
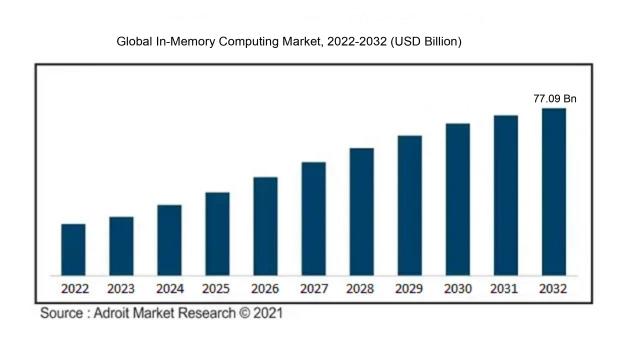
Businesses are able to accelerate the decision-making process by utilizing the data since in-memory cards procedures operate more quickly than disk-to-memory systems. Using in-memory technology, decision-makers may quickly and conveniently access the data they need. Since in-memory technology has been available, back-end systems and programmes must perform well and transmit data more quickly in order to meet consumer demand for intelligent, interactive experiences.
In Memory Computing Market Scope :
| Metrics | Details |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Historic Data | 2018-2022 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Study Period | 2018-2032 |
| Forecast Unit | Value (USD) |
| Revenue forecast in 2032 | US$ 77.09 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 7.12% during 2022-2032 |
| Segment Covered | by Components,By Organization Size ,By Vertical,by Region. |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America Middle East and Africa |
| Key Players Profiled | Salesforce.com Inc., Microsoft Corporation, Software AG, SAS Institute Inc., Oracle Corporation, TIBCO Software Inc, Fujitsu Limited, Intel Corporation, SAP SE, and International Business Machines Corporation. |
Market Definition
IMC stands for "In-Memory Computing," a method of computing that uses the main memory (RAM) of a computer rather than more conventional disk-based storage systems to process and store data.
The goal is to speed up data processing and analytics operations by utilizing the main memory's high speed and low latency properties. Traditional systems, on the other hand, frequently rely on reading and writing data to and from slower disc storage, which can cause noticeable delays. In IMC, data is stored in a format that the processor can access directly, enabling substantially quicker data retrieval and processing.
Because of the quicker processing and shorter data access times, this is especially advantageous for real-time or almost real-time processing applications like big data analytics, financial could trading, and more. Processing times are greatly decreased and system performance is enhanced since accessing data from RAM is considerably faster than obtaining it from a disc. IMC is a good fit for applications that demand speedy data processing and analysis, allowing organizations to act quickly based on current information.
Because joins and aggregations can be completed considerably more quickly in in-memory databases, they can effectively handle complicated analytical queries. With the help of IMC, businesses can swiftly analyze huge amounts of historical data to get insights into potential future patterns.
Key Market Segmentation

Insights on Component
The In-Memory Data Management Segment is Valued for the Highest Share
A form of DBMS known as an in-memory database management system (IMDBMS) primarily stores, maintains, and manipulates data in the system's primary memory. In addition to removing hard disc storage's latency and overhead, this reduces the instruction set needed to access data. Though it boosts performance, keeping data in memory requires expensive hardware. Keep just the data that is needed the most frequently in memory, and save the remainder on a disc, to make the most of in-memory storage while keeping costs low.
Insights on Vertical
The BFSI Segment Valued for the Highest Share
It is referred to as BFSI, or banking, financial services, and insurance. Multiprocessing, historically the domain of huge and powerful machines like supercomputers, mainframe computers, and servers, is a technique used by certain computers to divide their work over numerous CPUs in a multiprocessing setup. These days, it's easy to get personal computers and laptops with many processors and cores (several CPUs on a single integrated circuit), and as a result, their use in lower-end markets is rising. The CPU and PIM cores of the suggested architecture share the same physical memory area. The CPU offers two methods for accessing memory. Sending data from the CPU to the memory is done via the CPU cache.
Insights on Region
The Asia Pacific Region Accounted for the Highest Share
Due to the existence of several growing nations like China and India, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to have substantial growth throughout the projection period. Services like business process outsourcing (BPO) and knowledge process outsourcing (KPO) are well-known in these nations. A manufacturing base may be found in these nations. In order to make decisions, every business operation that is carried out generates a significant amount of data that must be stored, processed, and analyzed. The in-memory computing industry is expanding in the Asia-Pacific region as a result of rising investments from a number of technological companies.
Key Company Profiles
The key players operating in the in-memory computing market include Salesforce.com Inc., Microsoft Corporation, Software AG, SAS Institute Inc., Oracle Corporation, TIBCO Software Inc, Fujitsu Limited, Intel Corporation, SAP SE, and International Business Machines Corporation.
COVID-19 Impact and Market Status
Global economic upheavals brought on by the epidemic forced many organizations to postpone or scale down IT expenditures, including the adoption of cutting-edge tools like in-memory computing.
Disruptions in the hardware supply chain may have delayed implementation by limiting the supply of the high-performance memory modules needed for in-memory computing systems. Investments in innovative technology, such as making the switch to in-memory computing, may have been deprioritized or delayed by organizations dealing with financial difficulties.
Numerous companies saw that they needed to speed up their digital transformation initiatives in order to adjust to remote employment and shifting consumer behavior. The adoption of technology like in-memory computing to improve real-time data processing for improved decision-making may have been sparked by this.
During lockdowns, demand grew for products and services in the e-commerce, online entertainment, and remote collaboration tools sectors. The rapid processing of huge amounts of data in real-time by in-memory computing may have been used to enhance user experiences in many fields. For tracking and decision-making, governments and health organizations have to examine enormous volumes of pandemic-related data. This data may have been processed and examined more effectively using in-memory computing.
Latest Trends
1. Edge computing designs are integrating in-memory computing, enabling data to be processed and analyzed closer to the point of origination. This is especially crucial for real-time processing applications like IoT and industrial automation. IMC's integration with AI and machine learning technologies makes it possible for AI-driven applications to analyze data in real-time.
2. By enhancing both technologies' capabilities, this convergence enables quick decision-making based on current information. Real-time analytics are increasingly using in-memory databases, which allow companies to run sophisticated queries and extract information from massive datasets without experiencing the delay that comes with disk-based storage solutions. For high-frequency trading, risk analysis, fraud detection, and portfolio optimization, the financial sector uses IMC.
3. Applications like social network analysis, recommendation systems, and fraud detection are increasing the need for in-memory graph databases. Graph processing may reveal intricate patterns and correlations in data.
4. Some systems are using hybrid memory architectures, fusing novel memory types like persistent memory (like Intel Optane) with conventional memory. Larger in-memory datasets and better data durability are made possible by this.
5. Without the need to physically relocate or copy data, in-memory data virtualization offers easy access to and integration of data from diverse sources, offering a unified picture for real-time analytics.
Significant Growth Factors
Real-time data processing and analytics are necessary for businesses across all sectors to make prompt and educated choices. The capacity of in-memory computing to quickly handle massive amounts of data is in line with this demand for immediate insights.
The demand for systems that can manage enormous data volumes and enable real-time processing has increased as organizations go through digital transformation. This shift is aided by in-memory computing since it offers the required speed and performance. Large datasets need to be processed effectively due to the growing popularity of big data analytics.
IMC enables quicker inquiries and analysis, enabling businesses to more efficiently get value from their data. Huge volumes of data need to be handled at the edge for real-time decision-making as a result of the Internet of Things (IoT) expansion.
Businesses may now more easily acquire and deploy these capabilities without the need for expensive on-premises hardware thanks to cloud service providers that provide in-memory computing services. IMC is used by sectors including e-commerce, retail, and entertainment to analyze real-time data and offer seamless and personalized consumer experiences.
Restraining Factors
Large quantities of memory are often needed for in-memory computing, which can be costly. For some organizations, the expense of installing and maintaining the required hardware and software infrastructure may be a barrier.
In the event of a power outage or a system crash, in-memory data is volatile and subject to loss. It's still difficult to guarantee data safety and persistence, especially for applications that need to be durable. While scaling up the memory capacity in big systems can be complicated and expensive, in-memory computing can provide performance advantages.
The amount of data produced by numerous sources may be more than what can fit in the memory. Businesses must carefully manage their data to decide what should be kept in memory and what should be kept in alternative storage solutions. An in-memory system's data integration from numerous sources might be difficult and time-consuming.
Specialized knowledge is necessary for deploying and managing in-memory computing technologies. It might be challenging to find and keep individuals with knowledge of IMC technology.
Concerns concerning security and compliance are raised when sensitive data is stored in memory. It is essential to make sure that data is secure and complies with legal obligations.
Recent Developments in the Global In-Memory Computing Market: A Snapshot
• In January 2022, Samsung introduced the first in-memory computer platform built on MRAM (magnetoresistive random access memory), a type of non-volatile memory. Modern computing techniques like "in-memory computing" aim to store and analyze data in a memory network simultaneously. Next-generation low-power AI semiconductor computers might be realized using this technology, which is one of the potential ones. Samsung says that the new technology can process a large quantity of data contained inside the memory network itself without the need to transmit the data, and power consumption is also greatly lowered because the data processing in the memory network is carried out in a highly parallel way.
Key Segments
by Components Overview
• In-memory Data Management
• In-memory Application Platform
By Organization Size Overview
• Small & Medium Business
• Large Enterprise
By Vertical Overview
• BSFI
• Transportation
Regional Overview
North America
• U.S
• Canada
Europe
• Germany
• France
• UK
• Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
• China
• India
• Japan
• Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
• Mexico
• Brazil
• Rest of South America

