Market Analysis and Insights:
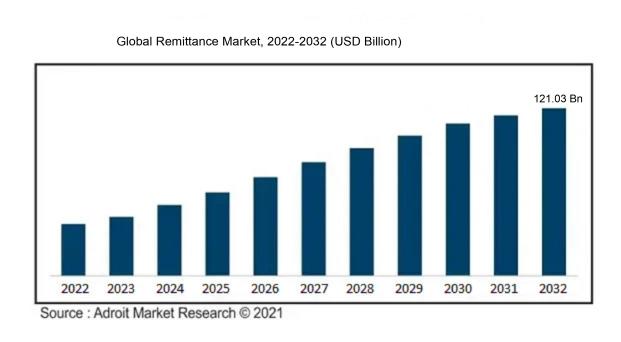
The global remittance market was estimated to be worth USD 50.13 billion in 2022, and from 2022 to 2032, it is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 3.89%, with an expected value of USD 121.03 billion in 2032.
The Remittance Market is driven by several factors. First and foremost, the growing number of migrants worldwide is a key driver. As more people leave their home countries in search of better job opportunities, they inevitably send money back to support their families and loved ones. Additionally, the increasing globalization and interconnectedness of economies have facilitated the expansion of international trade and employment, resulting in a higher demand for remittance services. Furthermore, advancements in technology and the rise of digital platforms have made it easier and more convenient to send and receive money across borders, fueling the growth of the remittance market. Additionally, government policies and regulatory initiatives that promote financial inclusion and reduce remittance costs also play a significant role in driving the market. Lastly, the strong emotional and cultural ties between migrants and their home countries act as a driving force, as individuals are often motivated by a sense of duty and responsibility to support their families and contribute to the development of their home economies. Overall, these factors contribute to the growth and sustenance of the remittance market.
Remittance Market Scope:
| Metrics | Details |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Historic Data | 2018-2022 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Study Period | 2018-2032 |
| Forecast Unit | Value (USD) |
| Revenue forecast in 2032 | USD 121.03 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 3.89% during 2022-2032 |
| Segment Covered | by Type,by Age group, By end-use ,by Region. |
| Regions Covered | By Mode of Transfer, By Type,By Channel,By End-use , By Region . |
| Key Players Profiled | Western Union, MoneyGram, Ria Financial Services, PayPal, TransferWise, WorldRemit, Xoom, OFX, Payoneer, and Remitly |
Market Definition
Remittance refers to the transfer of money or funds, usually from a person working in a foreign country back to their home country. It is a way for individuals to send financial support to their families or loved ones abroad.
Remittance plays a crucial role in the global economy, serving as a lifeline for many individuals and countries. Firstly, it is essential for millions of migrant workers who send money back to their families in their home countries, providing financial support for education, healthcare, and daily necessities. Remittance also contributes to poverty reduction by boosting the livelihoods and socio-economic well-being of the recipient families, ultimately enhancing local consumption and economic growth. Moreover, remittance is an important source of foreign exchange for developing nations, helping to stabilize currency values and promote economic stability. It enables nations to fund infrastructure development, improve public services, and enhance overall living standards. Additionally, remittance impacts global financial systems by encouraging the development of digital payment platforms and innovative financial services, promoting financial inclusion and facilitating financial integration. Therefore, acknowledging the significance of remittance is crucial for policymakers, as it can inform decisions to create favourable policies that optimize the benefits of remittance flows for both senders and receivers, fostering inclusive growth and sustainable development.
Key Market Segmentation:

Insights On Key Mode of Transfer
Digital
As per current trends and patterns, the Digital mode of transfer is expected to dominate the global remittance market. Thanks to advancements in technology and the growing digital literacy among users, these transfer methods are becoming widely accepted. They facilitate speedier, more secure, and cost-effective transactions, making them preferable among consumers who need to send or receive money.
Traditional (Non-digital)
Despite the dominance present in digital transfer, traditional, non-digital transfer methods continue to serve significant portions of the global remittance market. This method primarily consists of drafts, money orders, and other means of tangible transfers. Despite being less efficient and more time-consuming than their digital counterparts, these methods still thrive due to their trusted and reliable nature, and due to the significant amount of people who either don't have access to or don't trust digital methods.
Insights On Key Type
Inward
The Inward mode is predicted to lead the global remittance market predominantly. This dominance can mainly be attributed to the broad role it plays in the economies of many nations particularly developing countries, where it acts as an essential source of income for families and in some instances surpasses foreign aid. The increasing number of migrants worldwide, due to factors like better job opportunities and lifestyle changes, further propels this section, resulting in a positive effect on the market.
Outward
The Outward mode, though not as prominent as the Inward, still holds a significant place in the global remittance market. This mode involves sending money from the host country to the home country and is mainly used by businesses and corporations for overseas investments and payments. Although it may not dominate, it still contributes a considerable sum to the remittance market size due to the globalization of businesses.
Personal
The Personal type focuses on the transfer of funds between individuals, often by migrant workers sending money to families back home. This form of remittance is highly prevalent but is unlikely to dominate due to several factors such as transfer fees and sometimes, asylum policies. However, with the increase in cross-border mobility and digital payment options, personal remittances are beginning to see steady growth.
Small Businesses
Small Businesses contribute to the remittance market through international transactions for goods, services, or investments. This category is critical, particularly in supporting economies in developing countries, but its market share might be lesser due to factors like limited resources and less global reach compared to large corporations. However, the advent of digital financial services is projected to boost this category in the future.
Insights On Key Channel
Digital Money Transfer Platforms
Predicted changes in the Global Remittance market suggest that Digital Money Transfer Platforms will become the most influential sector. This is due to the ascension of technology and greater accessibility to digital tools globally. Their high competence in providing fast, secure, and low-cost services is enabling them to gain more popularity among different end-user categories.
Banks
Despite the rise of digital money transfer platforms, Banks will still play a considerable role in the Global Remittance market. Banks are seen as more reliable with a secure mode of transfer which captivates a significant user base, especially among the older population and big businesses. However, the higher costs associated and slower service could be limiting their growth in this market.
Online Wallets
Online Wallets are fast emerging as a popular alternative for global remittances, particularly for smaller and more frequent transfers. With the ever-increasing penetration of smartphones and internet connectivity, the online wallet market is poised for a big upheaval. This platform's agility, convenience, and instantaneous money transfer will likely drive increased adoption, particularly among younger demographics and small businesses.
Insights On Key End-use
As there is no specific data provided about the future predictions of the market, I'll provide general insights based on an understanding of the market trends.
Migrant Labor Workforce
This sector will likely dominate the Global Remittance market. This is because migrant labour, especially from developing countries to developed nations, typically sends a significant portion of their income back home. These remittances form a substantial part of the income of their families, thus making this sector a vital part of the global remittance market.
Personal
The personal sector of the global remittance market involves individuals sending money across borders for personal reasons like support of family members or remittance of earnings. While the personal sector is significant, it generally tends to be less consistent than remittances from the migrant labour force, as it relies heavily on individual circumstances and situations.
Small Businesses
Small businesses, who often engage in cross-border transactions, form another part of the Global Remittance market. The demand in this area comes from the transfer of funds for business expenses, payment to partners, and procurement of goods and services. While not as dominant as migrant labour, this field still contributes significantly to the market.
Others
The 'Others' sector could involve non-profit organizations, large corporations, or occasional personal transactions outside the aforementioned categories. The contribution of this sector is diverse and dependable on specific situations or events, so it is less predictable. However, it nonetheless forms a part of the Global Remittance market.
Insights on Regional Analysis:
North America: In the global remittance market, North America is expected to dominate due to its strong technological infrastructure and widespread acceptance of digital payment platforms. The region's well-established and secure banking systems, along with its high volume of international migration, contribute to its dominance. North America's emphasis on innovation and advanced financial technologies positions it as a leader in facilitating cross-border remittances, making it the preferred choice for individuals sending money overseas. With a large population of migrants and a favourable regulatory environment, North America continues to attract significant remittance flows.
South America: While South America may not dominate the global remittance market, it still holds significant potential for growth. The region's economic development, increasing access to financial services, and growing number of migrants contribute to its remittance market's expansion. South American countries such as Brazil, Colombia, and Argentina have seen a rise in remittances, driven by increased migration and diaspora communities. Efforts by governments and financial institutions to promote digital payment solutions and reduce transaction costs further enhance the region's remittance market's potential.
Asia Pacific: Asia Pacific is poised to become a major player in the global remittance market. With countries like China, India, and the Philippines experiencing high levels of migration, the region witnesses substantial remittance flows. The adoption of digital payment platforms, rapid technological advancements, and supportive government policies contribute to the growth of the remittance market in the Asia Pacific. Additionally, the development of innovative fintech solutions catering to the specific needs of migrants fuels the rise of the region as a dominant player in the global remittance landscape.
Europe: Although Europe may not dominate the global remittance market, it remains a significant player. The region's strong economies, extensive financial networks, and large migrant population contribute to its remittance market. European countries such as Germany, the United Kingdom, and France receive a substantial amount of remittances. Regulatory frameworks that promote competition and transparency in the remittance industry support the growth of digital payment platforms. With a focus on enhancing financial inclusion and facilitating seamless cross-border transactions, Europe continues to play a crucial role in the global remittance landscape.
Middle East & Africa: The Middle East & Africa region showcases immense potential in the global remittance market. The presence of large numbers of migrant workers and expatriate communities contributes to the growth of remittance flows. Countries like the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, and Kenya receive significant remittances. Despite challenges such as limited financial infrastructure and high costs, the region is witnessing the rapid adoption of digital payment solutions. Efforts by governments and financial institutions to improve access to financial services and reduce remittance costs further enhance the region's position in the global remittance market.
Company Profiles:
The key players in the global remittance market, such as Western Union, MoneyGram, and PayPal, serve as facilitators for individuals and businesses to send and receive money across borders, enabling secure and efficient international financial transactions.
Some key players in the remittance market include Western Union, MoneyGram, Ria Financial Services, PayPal, TransferWise, WorldRemit, Xoom, OFX, Payoneer, and Remitly. These companies specialize in facilitating the transfer of money between individuals and businesses across different countries and currencies. They offer various services such as online money transfers, mobile wallet transfers, cash pickup services, and more. With their extensive networks and easy-to-use platforms, these key players have become major players in the remittance market, providing individuals and businesses with secure and efficient ways to send and receive money internationally.
COVID-19 Impact and Market Status:
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the global remittance market, causing a decline in remittance flows due to economic disruptions and job losses. The closure of businesses and restrictions on movement have hindered migrant workers' ability to send money to their families, creating financial hardships for many households reliant on remittances.
The outbreak of COVID-19 has had a significant impact on the remittance market. Remittances, or money transfers made by migrants to their home countries, have been severely affected by the pandemic due to several factors. First, the global economic slowdown caused by the virus has led to job losses and income reduction among migrants, making it difficult for them to send money back home. Travel restrictions and lockdown measures imposed by governments have also disrupted the traditional remittance channels, such as physical cash transfers or in-person transactions, affecting the overall volume of remittances. Additionally, the closure of businesses, particularly in the hospitality and service sectors, has resulted in a decrease in demand for migrant workers, further dampening remittance flow. However, despite these challenges, the remittance market has seen a shift towards digital platforms and online transfers, with the use of mobile money and digital wallets on the rise. This has helped mitigate some of the negative impacts, ensuring that remittances continue to reach their intended recipients, albeit with some delays and changes in sending patterns. Overall, the COVID-19 pandemic has presented unprecedented challenges to the remittance market, but it has also accelerated the adoption of digital solutions, making the market more resilient in the long run.
Latest Trends and Innovation:
- In February 2020, Mastercard announced its acquisition of Transfast, a cross-border payments network, to enhance its global reach in the remittance market.
- In January 2022, PayPal completed the acquisition of Venmo, a popular peer-to-peer mobile payment platform, to expand its remittance offerings and strengthen its presence in the market.
- In November 2020, Western Union partnered with Crystal Blockchain, a subsidiary of Bitfury Group, to enhance its anti-money laundering efforts and improve compliance in remittance transactions.
- In September 2020, MoneyGram partnered with Ant Group, the parent company of Alipay, to enable faster and more convenient cross-border remittances for their users.
- In August 2019, Ripple, a blockchain technology company, acquired Algrim, an Icelandic trading firm, to bolster its liquidity and trading capabilities for global remittance payments.
- In July 2020, Wise (formerly TransferWise) became the first remittance service provider to be granted a license by the Bank of England to directly access the UK's real-time payments system.
- In June 2022, Western Union announced a partnership with Coins. ph, a leading cryptocurrency wallet provider in the Philippines, to enable seamless cash pickup and digital wallet transfers for Filipinos abroad.
- In March 2022, Ria Money Transfer joined forces with Thunes, a global cross-border payments network, to expand its reach into emerging markets and improve its remittance services.
- In May 2020, Remitly, a digital remittance platform, raised $85 million in Series F funding led by Prosus Ventures to support its expansion plans and further develop its technology.
- In April 2022, WorldRemit acquired Sendwave, a digital remittance company focused on the African market, to strengthen its presence in Africa and expand its customer base.
- In December 2019, Azimo partnered with Siam Commercial Bank (SCB) to launch an instant remittance service from Europe to Thailand, providing customers with faster and more affordable transfers.
Significant Growth Factors:
The growth factors of the Remittance Market include increasing globalization, technological advancements, and growing migration patterns.
The remittance market has witnessed significant growth in recent years and is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Several key factors have contributed to this growth. Firstly, the increasing number of international migrants has fueled the demand for remittance services. With globalization, more people are moving to different countries for work and better economic opportunities, resulting in a larger population sending money back to their home countries. Additionally, advancements in technology and the widespread use of smartphones have made it easier and more convenient for individuals to send money across borders. The rise of digital payment platforms and mobile banking has facilitated quick and secure transactions, further boosting the remittance market. Moreover, efforts by governments and financial institutions to promote financial inclusion have played a vital role in expanding the market. Initiatives such as reducing transaction costs, simplifying documentation requirements, and improving accessibility to banking services have made remittance services more accessible to a larger population, particularly in developing countries. Lastly, the COVID-19 pandemic has also contributed to the growth of the remittance market. As economic uncertainty and job losses have hit many countries, an increased reliance on remittance flows has been observed to support families and communities back home. In conclusion, factors such as the growing migrant population, technological advancements, financial inclusion efforts, and the impact of the pandemic have all played significant roles in driving the growth of the remittance market.
Restraining Factors:
The main challenges limiting growth in the remittance market include high transaction costs, regulatory and compliance requirements, and a lack of transparency and security.
The Remittance Market, while experiencing significant growth, faces several restraining factors that hinder its full potential. One major factor is the high transaction costs associated with money transfers, such as fees charged by transfer agents, foreign exchange losses, and other intermediary charges. These costs can be particularly burdensome for lower-income individuals who rely on remittances for their livelihoods. Additionally, limited access to financial services in some regions, especially in rural areas, makes it difficult for recipients to easily receive and utilize remittances. Moreover, regulatory barriers and compliance requirements, such as know-your-customer (KYC) procedures, can increase the complexity and cost of sending money across borders. Another significant challenge is the prevalence of informal remittance channels, especially in countries with underdeveloped financial systems, which can undermine the transparency and security of transactions. Finally, the remittance market is impacted by economic volatility and exchange rate fluctuations, adding risk and uncertainty to the process. Despite these challenges, it is important to note that efforts are being made to address these issues. Governments and financial institutions are working towards reducing transaction costs, expanding financial inclusion, and implementing stronger regulations. The growth potential of the remittance market, given its crucial role in contributing to economic development and poverty reduction, remains highly promising.
Key Segments of the Remittance Market
Remittance Market Overview
• Mode of Transfer
• Digital Remittance
• Traditional Remittance (Non-digital)
Type
• Inward Remittance
• Outward Remittance
• Channel
• Banks
• Money Transfer Platforms
• Online Platforms (Wallets)
End-use
• Migrant Labor Workforce
• Personal Use
• Small Businesses
• Others
Regional Overview
North America
• U.S.
• Canada
Europe
• Germany
• France
• UK
• Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
• China
• India
• Japan
• Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
• Mexico
• Brazil
• Rest of South America

