Market Analysis and Insights
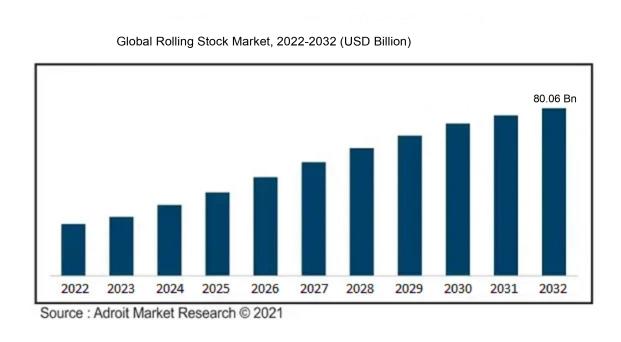
The size of the global Rolling Stock market, which was US$ 56.05 billion in 2022, is projected to increase by CAGR of 3.10% from 2022 to 2032 to reach US$ 80.06 billion by 2032.
A need for quicker and more effective trains has been generated by the expansion of intercity and high-speed rail networks. Because they use less energy storage and accelerate more quickly than diesel trains, electric trains are more suitable for high-speed transport. Given their cheaper fuel and maintenance expenses, electric trains can ultimately be more affordable than diesel ones. Governments and smart railway companies who wish to cut their transportation spending are drawn to these cost savings, which is causing the industry to expand.
Rolling Stock Market Scope:
| Metrics | Details |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Historic Data | 2018-2022 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Study Period | 2018-2032 |
| Forecast Unit | Value (USD) |
| Revenue forecast in 2032 | US$ 80.06 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 3.10% during 2022-2032 |
| Segment Covered | by Type,End-Use,By Region. |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America Middle East and Africa |
| Key Players Profiled | CRRC Corporation, Siemens Mobility, Trinity Rail, GE Transportation, Alstom, Wabtec Corporation, Hyundai Rotem, Kawasaki Heavy, Greenbrier, and Stadler Rail & Hitachi Rail System. |
Market Definition
The term "rolling stock" describes any train, tram, locomotive, or railcar that moves over a railway track. These vehicles enable the movement of people and goods over rail networks, making them a crucial component of the transportation infrastructure.
A crucial element of the railway sector, rolling stock is important for both local and long-distance transportation. These are made to convey people and frequently include multiple classes or compartments for varying degrees of comfort. High-speed trains over large distances and commuter trains for cities are both examples of passenger trains.
These are employed to move bulk commodities, manufactured items, and raw resources as cargo. Freight trains can be built using boxcars, flatcars, tank cars, and hopper cars, among other layouts. The propulsion and power required to move the rail wheels are provided by locomotives, which are strong vehicles. They have engines (often diesel or electric) that produce the force necessary to push or pull the train. Railcars are specialized automobiles made for certain uses. For instance, intermodal trains transport shipping containers, hopper cars carry bulk products, and tank cars transport liquids. These are intended for quick trips between cities and nations, frequently going much faster than regular trains. Passengers have access to effective and time-saving transit choices with high-speed trains.
As traffic congestion worsens in metropolitan areas and demand for public transport increases, government agencies are expected to make significant investments in building support infrastructure and bolstering already-existing infrastructure. These advancements will probably result in further rolling stock orders. On the other hand, the price of new rail vehicles is a barrier to investment and may function as a limitation. City traffic is suffocating under the weight of mounting environmental problems associated with air and car travel, and rail travel is a financially viable and environmentally sound alternative.
Key Market Segmentation

Insights on Type
The Diesel Segment Valued for the Highest Share
By type, the Diesel segment is predicted to retain the highest CAGR during the forecast period and occupy the largest share of the worldwide market in 2022. The market has expanded as a consequence of an expansion in the usage of diesel trucks for the transportation of heavy products in sectors including mining, manufacturing, and oil and gas. Outside diesel cars also offer advantages such as low cost and high torque engines. To meet the need for innovative rail cars, manufacturers like Corporation Limited, Bombardier Transportation CRRC, and Alstom Transport are producing turbocharged diesel.
Insights on Region
The APAC Region Accounted for the Highest Share
Due to the adoption of rail transport for both people and products, the Asia Pacific region now dominates the worldwide market and is expected to keep doing so during the projection period. The expansion of the regional market may also be attributable to the rising expenditures on electric trains and metro trains in nations like Taiwan, China, and India. The Middle East and Africa area is anticipated to have rapid growth throughout the projected period. Applications for the transportation of commodities are growing in the mining and oil and gas sectors, which is boosting the worldwide market for rolling stock. The growing utilization of rolling stock because of its high torque power and improved safety is another factor driving the area industry.
Key Company Profiles
The key players operating in the rolling stock market include CRRC Corporation, Siemens Mobility, Trinity Rail, GE Transportation, Alstom, Wabtec Corporation, Hyundai Rotem, Kawasaki Heavy, Greenbrier, and Stadler Rail & Hitachi Rail System.
COVID-19 Impact and Market Status
Lockdowns, travel restrictions, and plant closures hampered worldwide supply chains and impacted the manufacture of machinery and parts for rolling stock. Order and project completion becomes difficult as a result of supply chain delays.
Both long-distance and urban transit were impacted by the pandemic's lower demand for passenger travel. Lower demand for new rolling stock, notably for passenger trains and light rail cars, was caused by decreased ridership and travel limitations. Due to the pandemic's effects on production, logistics, and staff availability, several current rolling stock projects experienced delays.
As a result, project deadlines were extended. Budgets for the procurement of new rolling stock were impacted by economic instability and decreased income for train operators and transit authorities. Orders have to be postponed or cancelled due to financial restrictions.
Latest Trends
1. Real-time monitoring, data analysis, predictive maintenance, and increased communication between rolling stock and control centers are made possible by the integration of digital technology and networking solutions. Improved operational effectiveness and passenger safety result from this.
2. The creation of fully and partially autonomous railway systems seeks to boost productivity, lessen human error, and enhance train operations. To provide safe and accurate train control, these systems make use of cutting-edge sensors, AI, and automation technologies.
3. To lower greenhouse gas emissions and dependency on fossil fuels, more electrified rolling stock is being used, such as electric locomotives and battery-electric trains. Additionally, energy-saving technology like regenerative brakes and lightweight materials are being used.
4. As an alternative to battery-powered trains, hydrogen fuel cell technology is being investigated since it offers zero-emission propulsion and greater ranges.
5. To improve the passenger experience, passenger information systems offer real-time updates on routes, timetables, delays, and other pertinent information. These systems frequently have speech announcements, smartphone apps, and digital displays.
6. For quick and safe ticketing and passenger identification, biometric technology such as fingerprint and face recognition is employed.
Significant Growth Factors
The demand for effective and sustainable public transport networks is driven by rising urbanization and population expansion in many areas, which encourages the purchase of new rolling equipment.
There are prospects for the purchase of new vehicles as a result of the aging and need for replacement or modernization of many current rolling stock fleets.
The deployment of electric and hydrogen-powered rolling stock is being pushed by the emphasis on lowering greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable transportation modes. The need for new rolling equipment is sparked by investments in rail infrastructure, such as high-speed rail networks, urban transit systems, and intercity connections. The development of the rolling stock market is influenced by government initiatives, financial incentives, and financing plans aimed at enhancing public transit and easing traffic congestion. Rolling stock needs to be efficient and dependable in order to convey commodities, including cross-border trade and logistics.
The demand for different kinds of rolling stock, such as light tower rail vehicles and electric buses, is influenced by the development of ride-sharing, last-mile solutions, and mobility-as-a-service platforms.
Restraining Factors
Budget constraints for transit agencies, governments, and operators may result from the significant capital expenditures related to acquiring and maintaining rolling equipment.
Economic downturns and financial instability can have an influence on investment choices, causing rolling stock project delays or cancellations.
The creation and use of rolling stock can be complicated by regulatory issues like safety standards, interoperability requirements, and pollution laws.
Purchasing rolling stock entails intricate bidding procedures, discussions, and coordination amongst several parties, all of which have the potential to cause delays.
The availability of parts and supplies required for production can be impacted by disruptions in the global supply chain, as was the case during the COVID-19 epidemic.
Recent Developments in the Global Rolling Stock Market: A Snapshot
• In March 2023, the Egyptian Ministry of Transportation will give CISC Transmashholding (TMH), the leading Russian manufacturer of rolling equipment, a 12-year maintenance contract for 430 million euros. For a period of 12 years, TMH will provide technical support for the transportation of autos, as per the contract. TMH will also build a specialised rail depot in the outskirts of Cairo, equip it, train local employees, maintain the rolling stock, and provide replacement components.
Key Segments Rolling Stock Market
by Type
• Locomotive {Diesel Locomotives, Electric Locomotives, Electro-Diesel Locomotives and Others},
• Metro
• Monorail
• Trams
• Freight Wagon
• Passenger Coaches
• Others
End-Use Overview
• Passenger Transit
• Cargo Train
Regional Overview
North America
• U.S
• Canada
Europe
• Germany
• France
• UK
• Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
• China
• India
• Japan
• Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
• Mexico
• Brazil
• Rest of South America

