Market Analysis and Insights:
The market for Waste-to-Energy was estimated to be worth USD 44 billion in 2023, and from 2023 to 2033, it is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 7.5%, with an expected value of USD 89 billion in 2033.
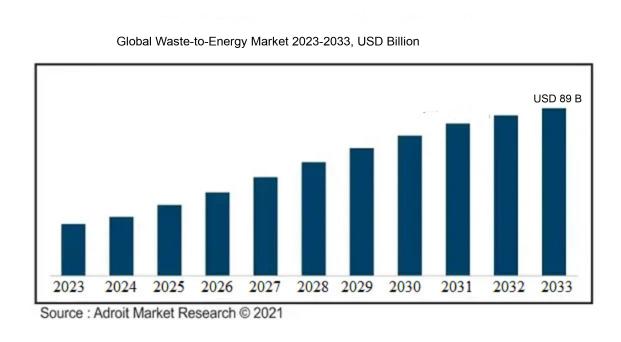
The Waste-to-Energy sector is propelled by several pivotal factors, such as rising waste production, the demand for sustainable waste management approaches, and the increasing need for energy. The effects of urbanization and population expansion result in elevated levels of municipal solid waste, which necessitates the implementation of effective disposal strategies. WtE technologies serve a dual purpose by not only reducing reliance on landfills but also by producing renewable energy, thereby supporting environmental sustainability objectives. Furthermore, government initiatives focused on minimizing carbon emissions and advancing circular economy practices enhance market development, as regulatory frameworks stimulate the establishment of WtE plants. In addition, advancements in waste processing and energy recovery technologies have optimized efficiency and affordability, making investments in WtE more appealing. Lastly, the growing public consciousness regarding environmental concerns fosters enthusiasm for renewable energy initiatives, further solidifying the attractiveness of the WtE market as a pragmatic response to modern waste management dilemmas.
Waste-to-Energy Market Scope :
| Metrics | Details |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Historic Data | 2020-2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2023-2033 |
| Study Period | 2022-2033 |
| Forecast Unit | Value (USD) |
| Revenue forecast in 2033 | USD 89 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 7.5% during 2023-2033 |
| Segment Covered | By Technology, By Form, By Application, Regions |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America, Middle East and Africa |
| Key Players Profiled | Veolia Environnement S.A., Covanta Holding Corporation, SUEZ Recycling and Recovery, Waste Management, Inc., Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc., Siemens AG, Hitachi Zosen Corporation, FCC Environment, Kineco Limited, and Enerkem Inc. Moreover, firms such as Constellation Energy, A2A S.p.A., DONG Energy A/S (currently known as Ørsted A/S), META Group. |
Market Definition
Waste-to-Energy encompasses the transformation of waste materials that cannot be recycled into valuable energy forms, such as electricity or heat, utilizing combustion and various technological methods. This strategy mitigates the volume of waste sent to landfills while simultaneously producing renewable energy, thus playing a significant role in promoting sustainable practices.
Waste-to-Energy plays a vital role in sustainable waste management by decreasing the reliance on landfills and mitigating environmental pollution. This method transforms organic waste into energy through techniques such as incineration and anaerobic digestion, producing electricity and heat, which serves as a renewable energy supply. This strategy not only eases the pressure on conventional waste disposal systems but also helps lower greenhouse gas emissions by reducing waste breakdown in landfills. Moreover, WtE fosters a circular economy by enhancing resource recovery and diminishing dependence on fossil fuels, thereby yielding cleaner energy alternatives and positively impacting public health.
Key Market Segmentation:
Insights On Key Technology
Thermal
Thermal technology is expected to dominate the Global Waste-to-Energy market primarily due to its established infrastructure and efficiency in converting waste materials into energy. This technology employs various processes, such as incineration and gasification, which can handle a wide range of waste types, including municipal solid waste and industrial refuse. The rising demand for renewable energy sources and the global push for sustainable waste management solutions further bolster the adoption of thermal technology. Its ability to produce high-quality energy in the form of electricity or heat makes it a more attractive option for many municipalities and companies aiming to reduce landfill usage and carbon footprints.
Biological
Biological technology, which includes methods like anaerobic digestion and fermentation, offers a sustainable approach to waste-to-energy conversion, particularly for organic materials. However, its growth has been somewhat constrained by limitations in feedstock availability and slower energy production rates compared to thermal methods. Despite these challenges, the increasing focus on biofuels and biogas as alternatives to fossil fuels may drive further advancements and adoption in this field. The environmentally friendly nature of biological treatment makes it appealing to companies looking to enhance sustainability practices and minimize the ecological impacts of waste.
Insights On Key Form
Electricity
Electricity is expected to dominate the Global Waste-to-Energy market due to the increasing demand for renewable energy sources and the global shift towards sustainability. The ability to convert waste materials into electricity not only helps in reducing landfill mass but also provides a viable power option for industries and municipalities. With technological advancements in anaerobic digestion and gasification processes, electricity generation from waste is becoming more efficient and economically viable. Furthermore, government incentives and support for renewable energy projects are fueling investments in waste-to-energy facilities that focus on electricity production, making it the leading form in the market.
Steam
Steam generation is another significant aspect of the Waste-to-Energy market, primarily utilized in industrial applications and district heating systems. This form involves using combustion processes to convert waste into steam, which can then be used for power generation or as a direct heating source. Its relevance is fueled by the need for industrial heat and process energy, especially in regions with high thermal energy demands. Additionally, steam systems are well-established, allowing existing infrastructure to be retrofitted for waste-to-energy conversion, further enhancing their utility in the market.
Hot Water
Hot water production through waste-to-energy conversion is typically aimed at residential and commercial heating applications. While it does have its niche, hot water systems are less prominent compared to electricity and steam forms. The demand for hot water systems arises mainly from heating needs in densely populated areas, which contributes to their market presence. However, the broader energy market dynamics tend to favor electricity and steam for larger-scale applications. Nevertheless, advancements in efficiency and technology may enable hot water systems to carve out a more substantial market share in the upcoming years.
Insights On Key Application
Generation of Energy
The Global Waste-to-Energy Market is expected to be predominantly driven by the Generation of Energy application. This focuses on converting waste materials into usable energy, which is becoming increasingly essential in a world that is moving towards sustainable practices. The growing demand for energy, coupled with stricter regulations concerning waste disposal and rising landfill costs, makes energy generation from waste more attractive. Moreover, technological advancements in waste-to-energy conversion processes are improving efficiency and reducing emissions, which appeal to both governments and corporations aiming for greener solutions. Consequently, the economic and environmental benefits of energy generation will fortify its leading position in the market.
Treatment of Waste
The Treatment of Waste application plays a significant role by addressing waste management challenges effectively. This involves various processes aimed at decomposing and recycling waste materials, thereby reducing their impact on the environment. With increasing urbanization and stringent waste management policies, municipalities and organizations are investing in advanced treatment technologies. These initiatives not only help meet legal requirements but also promote circular economy principles by ensuring that waste is treated and not merely discarded. Therefore, while important, this is currently overshadowed by the growing significance of energy generation from waste.
Reduction of Waste Volume
The Reduction of Waste Volume application is crucial for minimizing the overall environmental footprint of waste disposal. Public concern over landfill use and its associated negative implications has catalyzed efforts to develop technologies that effectively reduce waste. This approach aims to convert bulky waste into a smaller, manageable form, contributing significantly to more efficient waste handling and disposal processes. However, as societies increasingly transition towards circular economies, the focus is shifting towards energy production as a primary goal. Despite its importance, this is currently less dominant in terms of market growth compared to energy generation and treatment applications.
Insights on Regional Analysis:
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific is poised to dominate the Global Waste-to-Energy market due to its rapid urbanization, growing population, and increasing waste generation. Countries like China and India are investing heavily in waste management technologies, aiming to reduce energy dependency and mitigate environmental concerns. The implementation of stringent regulations governing waste disposal and a rising awareness regarding sustainable energy sources bolster market growth in this region. Additionally, advancements in technology and significant investments from both public and private sectors further enhance the region's robust capacity in waste-to-energy initiatives, making it a frontrunner in this industry.
North America
North America holds a significant share in the Global Waste-to-Energy market, primarily driven by established waste management infrastructure and stringent environmental regulations. The region has witnessed substantial investments in advanced waste processing technologies, emphasizing sustainable practices. Furthermore, the increasing focus on reducing landfill waste and converting waste into renewable energy sources further propels market growth. The collaboration between governmental bodies and private enterprises fosters innovation and efficiency in waste-to-energy projects, establishing North America as a strong contender in the global landscape.
Europe
Europe is an important player in the Global Waste-to-Energy market, characterized by a mature waste management system and ambitious sustainability targets. The European Union has implemented various directives aimed at promoting circular economy practices, including waste-to-energy conversion. Countries like Sweden and Germany lead the way in integrating waste management with energy recovery, utilizing advanced technologies to optimize efficiency. This region's commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels catalyzes further investments and innovation, solidifying Europe's role in advancing waste-to-energy initiatives.
Latin America
Latin America is gradually emerging in the Global Waste-to-Energy market, influenced by urban expansion and increasing waste challenges. Several countries are beginning to recognize the potential of waste-to-energy solutions as a means to address waste disposal issues while generating renewable energy. Key initiatives implemented by governments and private sectors are aimed at boosting infrastructure and technology in this region. However, the market remains relatively untapped compared to other regions, with further growth potential hinging on investments and policy support to drive waste management innovations.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region is still developing its presence in the Global Waste-to-Energy market but faces significant challenges, including a lack of infrastructure and investment. However, growing urbanization and an increasing waste crisis are prompting countries to explore sustainable waste management solutions. Some nations are starting to implement waste-to-energy technologies to address both waste disposal and energy needs. Enhanced regional cooperation and foreign investments can foster growth, but substantial infrastructural and regulatory support will be crucial for the market to achieve its full potential in this region.
Company Profiles:
Prominent stakeholders in the global Waste-to-Energy market, encompassing technology innovators, service operators, and waste management firms, work together to transform both municipal and industrial waste into energy resources. Their efforts are directed toward fostering innovation, adhering to regulations, and optimizing processes to enhance sustainability and profitability within waste processing.
Prominent entities in the Waste-to-Energy sector encompass Veolia Environnement S.A., Covanta Holding Corporation, SUEZ Recycling and Recovery, Waste Management, Inc., Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc., Siemens AG, Hitachi Zosen Corporation, FCC Environment, Kineco Limited, and Enerkem Inc. Moreover, firms such as Constellation Energy, A2A S.p.A., DONG Energy A/S (currently known as Ørsted A/S), META Group, and Fundy Recycling make substantial impacts. Other distinguished organizations include Vattenfall AB, Recovered Energy, and Phoenix Energy. These companies are vital to advancing and executing waste management strategies and technologies within the global Waste-to-Energy landscape.
COVID-19 Impact and Market Status:
The Covid-19 pandemic profoundly impacted the Global Waste-to-Energy sector, causing project delays and a decrease in the availability of feedstock as a result of lockdown measures and economic downturns.
The COVID-19 crisis had a profound effect on the waste-to-energy sector, primarily by hampering waste collection and processing activities amid lockdowns and health protocols. With a significant decline in industrial operations and waste production during the of the pandemic, many facilities faced substantial operational hurdles. Furthermore, disruptions in the supply chain hindered the access to essential components and technologies necessary for the functioning of waste-to-energy plants. Nevertheless, this challenging period highlighted the critical need for sustainable waste management solutions, sparking renewed interest in waste-to-energy systems as nations worked towards greener recovery initiatives. As governments formulate sustainable post-pandemic recovery strategies, it is anticipated that investments in the waste-to-energy domain will increase, facilitating the modernization of infrastructure and improving energy recovery from waste. In conclusion, while the immediate repercussions of the pandemic were detrimental due to operational interruptions, the future prospects for the waste-to-energy industry appear promising, as it aligns with global environmental objectives.
Latest Trends and Innovation:
- In January 2021, Covanta Holding Corporation completed a merger with EQT Infrastructure, forming a partnership focused on waste-to-energy solutions and the advancement of sustainable waste management practices.
- In April 2021, Veolia and SUEZ finalized their merger, creating a global leader in environmental services, which aims to enhance waste-to-energy operations and improve resource recovery efficiencies.
- In March 2022, Waste Management, Inc. announced the acquisition of the landfill assets of Class 1 Waste Solutions, expanding its waste-to-energy capabilities and increasing its operational footprint in Texas.
- In August 2022, Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy unveiled a new technology that enhances energy recovery from waste by integrating its wind turbine technologies with waste-to-energy plants, promoting efficiency in energy generation.
- In November 2022, it was reported that the Swedish company Nordic Waste Management partnered with HZI (Hitachi Zosen Inova) to develop advanced waste-to-energy facilities in Scandinavia, focusing on innovative thermal treatment technologies.
- In February 2023, Bin2Barrel launched its proprietary technology aimed at converting plastic waste into synthetic fuels, representing a significant innovation within the waste-to-energy sector.
- In July 2023, the European Investment Bank announced funding for the construction of a new waste-to-energy plant by the French company Urbaser, highlighting the commitment to sustainable waste management and energy recovery.
- In September 2023, DBD Energy Ltd. developed a cutting-edge technology that converts waste into hydrogen gas for renewable energy generation, receiving investment to further advance the commercial viability of this innovation.
Significant Growth Factors:
The expansion of the Waste-to-Energy sector is driven by the rising volume of waste production, escalating energy requirements, and an increasing focus on environmentally sustainable waste management strategies.
The Waste-to-Energy sector is witnessing substantial expansion, propelled by multiple influential elements. Primarily, there is a growing global focus on ecological sustainability and effective waste management strategies, which has increased the appeal of converting discarded materials into energy, thereby decreasing reliance on landfills. Governments across the globe are enacting more rigorous waste management policies and promoting renewable energy projects, which in turn stimulates investment in WtE technologies.
Moreover, the rise in urban populations and rapid urbanization fuels greater waste production, necessitating the development of efficient waste processing and energy generation methods. Innovations in technologies such as incineration, gasification, and anaerobic digestion significantly improve the efficiency and practicality of WtE facilities, rendering them more appealing for energy recovery initiatives.
Additionally, the unpredictability of fossil fuel prices, along with international pledges to curtail greenhouse gas emissions, is accelerating the transition to alternative energy solutions, including WtE. The principles of a circular economy, which emphasize resource recovery and waste reduction, are also vital in broadening the scope of WtE implementations. Furthermore, ened public awareness and acceptance regarding renewable energy enhance the industry's prospects, fostering an encouraging environment for investments and advancements in this field. Altogether, these dynamics are poised to drive considerable growth in the Waste-to-Energy market in the years ahead.
Restraining Factors:
The Waste-to-Energy market faces several significant obstacles, including substantial initial investment requirements, regulatory hurdles, and public resistance stemming from environmental apprehensions.
The Waste-to-Energy sector encounters numerous challenges that may impede its expansion and broad acceptance. Primarily, the significant initial capital outlay required for constructing WtE facilities can discourage prospective investors, especially in developing areas where financial resources are scarce. Furthermore, the presence of regulatory barriers and rigorous environmental regulations can complicate the process of obtaining project approvals and elevate operating expenses. Public resistance, often characterized by NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) attitudes, can arise as local residents express apprehension about emissions and possible health implications associated with WtE plants. In addition, the market potential for WtE technologies can be constrained by rival waste management options, such as recycling and composting. Operational difficulties, including variability in feedstock and the intricate technology needed for waste conversion into energy, contribute further to these challenges. Nonetheless, advancements in technology, along with a growing emphasis on sustainability and circular economy models, are fostering innovative approaches, suggesting a pathway for the WtE market to thrive. Increased public awareness of renewable energy and supportive governmental initiatives can create a conducive environment for future growth in this field, integrating waste management with energy production in a sustainable manner.
Key Segments of the Waste-to-Energy Market
By Technology
• Thermal
• Biological
By Form
• Steam
• Electricity
• Hot Water
By Application
• Treatment of Waste
• Reduction of Waste Volume
• Generation of Energy
Regional Overview
North America
• US
• Canada
• Mexico
Europe
• Germany
• France
• U.K
• Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
• China
• Japan
• India
• Rest of Asia Pacific
Middle East and Africa
• Saudi Arabia
• UAE
• Rest of Middle East and Africa
Latin America
• Brazil
• Argentina
• Rest of Latin America

